Algorithm
Problem link- https://www.spoj.com/problems/TAXI/
TAXI - Taxi
In New Town all streets are built as straight lines intersecting at right angles at fixed distances, with the distance between intersections being a fixed 200 meters (see picture below).
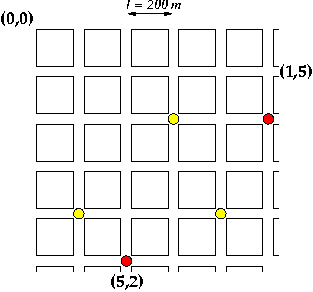
One of of the major events in New Town is the New Town Festival and nearly everybody wants to get a ticket. To give everyone the same chance of getting one of the few tickets the place and time of the advance sale are kept secret until some minutes before the ticket counter opens. Once the opening of the ticket counter is disclosed (by radio to give everyone a fair chance) everyone interested in getting some tickets tries to get to the counter immediately.
One of the most profiting citizens of this ticket selling procedure is New Town's taxi service owner. At the time of the radio announcement all over the town people ring up the taxi central and ask for a ride. The problem for the taxi central is that a lot of people ask for a ride at the same time and that the taxis have to pick up the people very quickly.
Your task is to help the taxi central finding out how many passengers can be transported to the ticket counter. You have to adhere to following constraints:
- each taxi can only take one passenger
- passengers always wait at intersections of roads
- at the time of the radio broadcast all taxis also wait at intersections
- the taxi has to reach the passenger within a given time limit (otherwise he will be too late to get a ticket)
Input
The first line contains the number of testcases k (k<=250). The first line of each testcase contains the number of persons p (1<=p<=400), the number of taxicabs t (1<=t<=200) the speed s (1<=s<=2000) of the taxis in meters per seconds and the time c to collect a person in seconds (1<=c<=1000000). The next p lines contains the position of the persons. The next t lines contain the position of the taxicabs in the city.
Output
For each testcase output the maximal number of persons that can be picked up.
Example
Input: 1 2 3 10 40 2 5 5 2 2 3 4 1 4 4 Output: 2
Code Examples
#1 Code Example with C++ Programming
Code -
C++ Programming
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
#define MOD 1000000007LL
#define EPS 1e-9
#define io ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(NULL);
#define M_PI 3.14159265358979323846
#define NIL 0
#define INF 1 << 28
template <typename T> T gcd(T a, T b){return (b==0)?a:gcd(b,a%b);}
template <typename T> T lcm(T a, T b){return a*(b/gcd(a,b));}
template <typename T> T mod_exp(T b, T p, T m){T x = 1;while(p){if(p&1)x=(x*b)%m;b=(b*b)%m;p=p>>1;}return x;}
template <typename T> T invFermat(T a, T p){return mod_exp(a, p-2, p);}
template <typename T> T exp(T b, T p){T x = 1;while(p){if(p&1)x=(x*b);b=(b*b);p=p>>1;}return x;}
const int MAXN = 1000;
vector<int> adj[MAXN];
int n, m, match[MAXN], dist[MAXN];
bool bfs(){ // returns true if there is an augmenting path
queue<int> q;
for(int i = 1;i <= n; i++){
if(match[i] == NIL){
dist[i] = 0;
q.push(i);
}
else
dist[i] = INF;
}
dist[NIL] = INF;
while(!q.empty()){
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
if(u != NIL){
for(auto v : adj[u]){
if(dist[match[v]] == INF){
dist[match[v]] = dist[u] + 1;
q.push(match[v]);
}
}
}
}
return (dist[NIL] != INF);
}
// returns true if there is an augmenting path beginning with free vertex u
bool dfs(int u){
if(u != NIL){
for(auto v : adj[u]){
if(dist[match[v]] == dist[u] + 1){
if(dfs(match[v])){
match[v] = u;
match[u] = v;
return true;
}
}
}
// if there is no augmenting path beginning with u.
dist[u] = INF;
return false;
}
return true;
}
int hopcroft_karp(){
int matching = 0;
// match is assumed to be NIL for all vertices
while(bfs())
for(int i = 1;i <= n; i++)
if(match[i] == NIL && dfs(i))
matching++;
return matching;
}
int distance(pair<int, int> p1, pair<int, int> p2){
return abs(p2.first - p1.first) + abs(p2.second - p1.second);
}
int main(){
io;
int k;
cin >> k;
while(k--){
memset(match, 0, sizeof match);
for(int i = 0;i <= 900; i++)
adj[i].clear();
int s, c;
cin >> n >> m >> s >> c;
pair < int, int> persons[n+1], taxis[m+1];
for(int i = 1;i <= n; i++){
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
persons[i] = {x, y};
}
for(int i = 1;i <= m; i++){
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
taxis[i] = {x, y};
}
for(int i = 1;i <= n; i++){
for(int j = 1;j <= m; j++){
pair < int, int> p1 = persons[i];
pair<int, int> p2 = taxis[j];
if(distance(p1, p2) <= s*c/200){
// cout << i << " " << j << endl;
adj[i].push_back(j+n);
}
}
}
cout << hopcroft_karp() << endl;
}
return 0;
}Input
2 3 10 40
2 5
5 2
2 3
4 1
4 4
Output
Demonstration
SPOJ Solution-Taxi-Solution in C, C++, Java, Python
