Algorithm
Problem Name: Data Structures -
In this HackerRank in Data Structures -
Alexa has two stacks of non-negative integers, stack a[n] and stack b[m] here index 0 denotes the top of the stack. Alexa challenges Nick to play the following game:
- In each move, Nick can remove one integer from the top of either stack a or stack b.
- Nick keeps a running sum of the integers he removes from the two stacks.
- Nick is disqualified from the game if, at any point, his running sum becomes greater than some integer maxSum given at the beginning of the game.
- Nick's final score is the total number of integers he has removed from the two stacks.
Given a,b and maxSum for 9 games, find the maximum possible score Nick can achieve.
Example
a = [1,2,3,4,5]
b = [6,7,8,9]
The maximum number of values Nick can remove is 4. here are two sets of choices with this result.
- Remove 1,2,3,4 from a with a sum of 10.
- Remove 1,2,3 from a and 6 from b with a sum of 12.
Function Description
Complete the twoStacks function in the editor below.
twoStacks has the following parameters: - int maxSum: the maximum allowed sum
- int a[n]: the first stack
- int b[m]: the second stack
Returns
- int: the maximum number of selections Nick can make
Input Format
The first line contains an integer, 9 (the number of games). The 3 - g subsequent lines describe each game in the following format:
- The first line contains three space-separated integers describing the respective values of n (the number of integers in stack a), m (the number of integers in stack b), and maxSum (the number that the sum of the integers removed from the two stacks cannot exceed).
- The second line contains n pace-separated integers, the respective values of a[i].
- The third line contains m space-separated integers, the respective values of b[i].
Constraints
- 1 <= g <= 50
- 1 <= n,m <= 10**5
- 0 <= a[i],b[i] <= 10**6
- 1 <= maxSum <= 10**6
Subtasks
- 1 <= n,m <= 100 for 50% of the maximum score.
Sample Input 0
1
5 4 10
4 2 4 6 1
2 1 8 5
Sample Output 0
4
Explanation 0
The two stacks initially look like this:
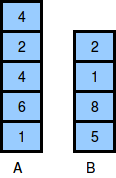
The image below depicts the integers Nick should choose to remove from the stacks. We print 4 as our answer, because that is the maximum number of integers that can be removed from the two stacks without the sum exceeding x = 10.
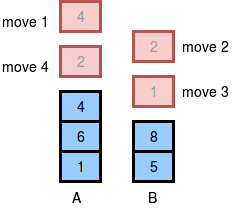
(There can be multiple ways to remove the integers from the stack, the image shows just one of them.)
Code Examples
#1 Code Example with C++ Programming
Code -
C++ Programming
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
string ltrim(const string &);
string rtrim(const string &);
vector < string> split(const string &);
/*
* Complete the 'twoStacks' function below.
*
* The function is expected to return an INTEGER.
* The function accepts following parameters:
* 1. INTEGER maxSum
* 2. INTEGER_ARRAY a
* 3. INTEGER_ARRAY b
*/
int twoStacks(int x, vector<int> a, vector<int> b) {
int sum = 0,i=0,j=0,ii=a.size(),jj=b.size() , cnt=0;
while(i < ii && sum+a[i]<=x)
sum+=a[i++];
cnt = i;
while(i>=0 && j < jj)
{
sum+=b[j++];
while(sum>x && i>0)
sum-=a[--i];
if(sum<=x && (i+j>>cnt)
cnt = i+j;
}
return cnt;
}
int main()
{
ofstream fout(getenv("OUTPUT_PATH"));
string g_temp;
getline(cin, g_temp);
int g = stoi(ltrim(rtrim(g_temp)));
for (int g_itr = 0; g_itr < g; g_itr++) {
string first_multiple_input_temp;
getline(cin, first_multiple_input_temp);
vector < string> first_multiple_input = split(rtrim(first_multiple_input_temp));
int n = stoi(first_multiple_input[0]);
int m = stoi(first_multiple_input[1]);
int maxSum = stoi(first_multiple_input[2]);
string a_temp_temp;
getline(cin, a_temp_temp);
vector < string> a_temp = split(rtrim(a_temp_temp));
vector<int> a(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int a_item = stoi(a_temp[i]);
a[i] = a_item;
}
string b_temp_temp;
getline(cin, b_temp_temp);
vector < string> b_temp = split(rtrim(b_temp_temp));
vector<int> b(m);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int b_item = stoi(b_temp[i]);
b[i] = b_item;
}
int result = twoStacks(maxSum, a, b);
fout << result << "\n";
}
fout.close();
return 0;
}
string ltrim(const string &str) {
string s(str);
s.erase(
s.begin(),
find_if(s.begin(), s.end(), not1(ptr_fun < int, int>(isspace)))
);
return s;
}
string rtrim(const string &str) {
string s(str);
s.erase(
find_if(s.rbegin(), s.rend(), not1(ptr_fun < int, int>(isspace))).base(),
s.end()
);
return s;
}
vector < string> split(const string &str) {
vector<string> tokens;
string::size_type start = 0;
string::size_type end = 0;
while ((end = str.find(" ", start)) != string::npos) {
tokens.push_back(str.substr(start, end - start));
start = end + 1;
}
tokens.push_back(str.substr(start));
return tokens;
}
#2 Code Example with Java Programming
Code -
Java Programming
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int g = sc.nextInt();
for (int tc = 0; tc < g; tc++) {
int n = sc.nextInt();
int m = sc.nextInt();
int x = sc.nextInt();
int[] a = readArray(sc, n);
int[] b = readArray(sc, m);
System.out.println(solve(a, b, x));
}
sc.close();
}
static int[] readArray(Scanner sc, int size) {
int[] result = new int[size];
for (int i = 0; i < result.length; i++) {
result[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
return result;
}
static int solve(int[] a, int[] b, int x) {
int lengthB = 0;
int sum = 0;
while (lengthB < b.length && sum + b[lengthB] <= x) {
sum += b[lengthB];
lengthB++;
}
int maxScore = lengthB;
for (int lengthA = 1; lengthA < = a.length; lengthA++) {
sum += a[lengthA - 1];
while (sum > x && lengthB > 0) {
lengthB--;
sum -= b[lengthB];
}
if (sum > x) {
break;
}
maxScore = Math.max(maxScore, lengthA + lengthB);
}
return maxScore;
}
}
#3 Code Example with Python Programming
Code -
Python Programming
#!/bin/python3
import sys
g = int(input().strip())
for a0 in range(g):
n,m,x = input().strip().split(' ')
n,m,x = [int(n),int(m),int(x)]
a = list(map(int, input().strip().split(' ')))
b = list(map(int, input().strip().split(' ')))
a = a[::-1]
b = b[::-1]
handy_stack = []
el_count = 0
total = 0
while len(a) > 0:
if total + a[-1] <= x:
temp = a.pop()
handy_stack.append(temp)
total += temp
el_count += 1
else:
break
total_b = 0
while len(b) > 0:
if total_b + b[-1] <= x:
if total + b[-1] <= x:
temp = b.pop()
total += temp
total_b += temp
el_count += 1
else:
temp = b.pop()
total = total - handy_stack.pop() + temp
total_b += temp
else:
break
print(el_count)
