Algorithm
Bob is about to take a hot bath.
There are two taps to fill the bath: a hot water tap and a cold water tap. The cold water's temperature is t1, and the hot water's temperature is t2. The cold water tap can transmit any integer number of water units per second from 0 to x1, inclusive. Similarly, the hot water tap can transmit from 0 to x2 water units per second.
If y1 water units per second flow through the first tap and y2 water units per second flow through the second tap, then the resulting bath water temperature will be:
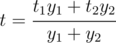
Bob wants to open both taps so that the bath water temperature was not less than t0. However, the temperature should be as close as possible to this value. If there are several optimal variants, Bob chooses the one that lets fill the bath in the quickest way possible.
Determine how much each tap should be opened so that Bob was pleased with the result in the end.
You are given five integers t1, t2, x1, x2 and t0 (1 ≤ t1 ≤ t0 ≤ t2 ≤ 106, 1 ≤ x1, x2 ≤ 106).
Print two space-separated integers y1 and y2 (0 ≤ y1 ≤ x1, 0 ≤ y2 ≤ x2).
10 70 100 100 25
99 33
300 500 1000 1000 300
1000 0
143 456 110 117 273
76 54
In the second sample the hot water tap shouldn't be opened, but the cold water tap should be opened at full capacity in order to fill the bath in the quickest way possible.
Code Examples
#1 Code Example with C++ Programming
Code -
C++ Programming
#include <iostream>
int main(){
int64_t t1, t2, x1, x2,t0; std::cin >> t1 >> t2 >> x1 >> x2 >> t0;
double best = 1e15;
int64_t y1, y2;
while(x1 >= 0 && x2 >= 0){
double t = (1.0 * t1 * x1 + 1.0 * t2 * x2) / ( 1.0 * x1 + 1.0 * x2);
if(t < t0){x1--; continue;}
if(t < best){best = t; y1 = x1; y2 = x2;}
x2--;
}
std::cout << y1 << " " << y2 << std::endl;
return 0;
}Input
Output
Demonstration
Codeforces Solution-A. Hot Bath-Solution in C, C++, Java, Python
