Algorithm
Musicians of a popular band "Flayer" have announced that they are going to "make their exit" with a world tour. Of course, they will visit Berland as well.
There are n cities in Berland. People can travel between cities using two-directional train routes; there are exactly m routes, i-th route can be used to go from city vi to city ui (and from ui to vi), and it costs wi coins to use this route.
Each city will be visited by "Flayer", and the cost of the concert ticket in i-th city is ai coins.
You have friends in every city of Berland, and they, knowing about your programming skills, asked you to calculate the minimum possible number of coins they have to pay to visit the concert. For every city i you have to compute the minimum number of coins a person from city i has to spend to travel to some city j (or possibly stay in city i), attend a concert there, and return to city i (if j ≠ i).
Formally, for every 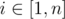 you have to calculate
you have to calculate 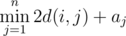 , where d(i, j) is the minimum number of coins you have to spend to travel from city i to city j. If there is no way to reach city j from city i, then we consider d(i, j) to be infinitely large.
, where d(i, j) is the minimum number of coins you have to spend to travel from city i to city j. If there is no way to reach city j from city i, then we consider d(i, j) to be infinitely large.
The first line contains two integers n and m (2 ≤ n ≤ 2·105, 1 ≤ m ≤ 2·105).
Then m lines follow, i-th contains three integers vi, ui and wi (1 ≤ vi, ui ≤ n, vi ≠ ui, 1 ≤ wi ≤ 1012) denoting i-th train route. There are no multiple train routes connecting the same pair of cities, that is, for each (v, u) neither extra (v, u) nor (u, v) present in input.
The next line contains n integers a1, a2, ... ak (1 ≤ ai ≤ 1012) — price to attend the concert in i-th city.
Print n integers. i-th of them must be equal to the minimum number of coins a person from city i has to spend to travel to some city j (or possibly stay in city i), attend a concert there, and return to city i (if j ≠ i).
4 2
1 2 4
2 3 7
6 20 1 25
6 14 1 25
3 3
1 2 1
2 3 1
1 3 1
30 10 20
12 10 12
Code Examples
#1 Code Example with C++ Programming
Code -
C++ Programming
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int const N = 2e5 + 1;
int n, m, a, b, fr;
long long c, tik[N], cost[N];
bool vis[N];
vector<vector<pair<int, long long> > > g;
priority_queue<pair<long long, int> > pq;
void Dijkstra() {
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
pq.push(make_pair(-tik[i], i));
cost[i] = tik[i];
}
int size;
while(!pq.empty()) {
size = pq.size();
while(size-- != 0) {
fr = pq.top().second;
c = -pq.top().first;
pq.pop();
if(vis[fr])
continue;
vis[fr] = true;
for(int i = 0; i < g[fr].size(); ++i) {
if(g[fr][i].second + c < cost[g[fr][i].first]) {
cost[g[fr][i].first] = g[fr][i].second + c;
pq.push(make_pair(-cost[g[fr][i].first], g[fr][i].first));
}
}
}
}
}
int main() {
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
g.resize(n);
for(int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
scanf("%d %d %lld", &a, &b, &c);
--a, --b;
g[a].push_back(make_pair(b, c * 2));
g[b].push_back(make_pair(a, c * 2));
}
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
scanf("%lld", tik + i);
Dijkstra();
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
printf("%s%lld", i ? " " : "", cost[i]);
return 0;
}Input
1 2 4
2 3 7
6 20 1 25
Output
Demonstration
Codeforces Solution-Buy a Ticket-Solution in C, C++, Java, Python
