Algorithm
You are given a system of pipes. It consists of two rows, each row consists of n pipes. The top left pipe has the coordinates (1,1) and the bottom right — (2,n).
There are six types of pipes: two types of straight pipes and four types of curved pipes. Here are the examples of all six types:
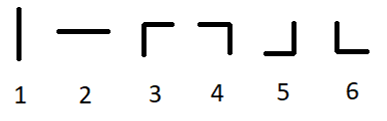 Types of pipes
Types of pipesYou can turn each of the given pipes 90 degrees clockwise or counterclockwise arbitrary (possibly, zero) number of times (so the types 1 and 2 can become each other and types 3,4,5,6 can become each other).
You want to turn some pipes in a way that the water flow can start at (1,0) (to the left of the top left pipe), move to the pipe at (1,1), flow somehow by connected pipes to the pipe at (2,n) and flow right to (2,n+1).
Pipes are connected if they are adjacent in the system and their ends are connected. Here are examples of connected pipes:
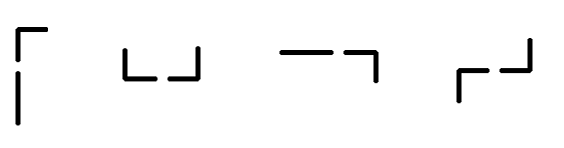 Examples of connected pipes
Examples of connected pipesLet's describe the problem using some example:
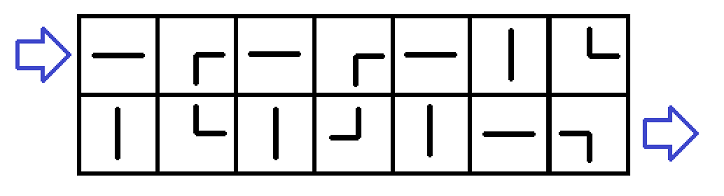 The first example input
The first example inputAnd its solution is below:
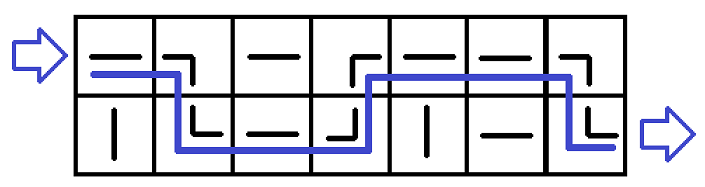 The first example answer
The first example answerAs you can see, the water flow is the poorly drawn blue line. To obtain the answer, we need to turn the pipe at (1,2) 90 degrees clockwise, the pipe at (2,3) 90 degrees, the pipe at (1,6) 90 degrees, the pipe at (1,7) 180 degrees and the pipe at (2,7) 180 degrees. Then the flow of water can reach (2,n+1) from (1,0).
You have to answer q independent queries.
The first line of the input contains one integer q (1≤q≤104) — the number of queries. Then q queries follow.
Each query consists of exactly three lines. The first line of the query contains one integer n (1≤n≤2⋅105) — the number of pipes in each row. The next two lines contain a description of the first and the second rows correspondingly. Each row description consists of n digits from 1 to 6 without any whitespaces between them, each digit corresponds to the type of pipe in the corresponding cell. See the problem statement to understand which digits correspond to which types of pipes.
It is guaranteed that the sum of n over all queries does not exceed 2⋅105.
For the i-th query print the answer for it — "YES" (without quotes) if it is possible to turn some pipes in a way that the water flow can reach (2,n+1) from (1,0), and "NO" otherwise.
6 7 2323216 1615124 1 3 4 2 13 24 2 12 34 3 536 345 2 46 54
YES YES YES NO YES NO
The first query from the example is described in the problem statement.
Code Examples
#1 Code Example with C++ Programming
Code -
C++ Programming
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int const N = 4e5 + 10;
char tmp;
int q, n, a[N];
int main() {
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("in", "r", stdin);
#endif
scanf("%d", &q);
for(int i = 0; i < q; ++i) {
scanf("%d", &n);
for(int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
scanf(" %c", &tmp);
a[j] = tmp - '0';
}
for(int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
scanf(" %c", &tmp);
a[n + j] = tmp - '0';
}
if(a[0] <= 2)
a[0] = 2;
else
a[0] = 4;
int row = 0, col = 1, frow = 0, fcol = 0, trow, tcol;
if(a[0] == 4)
row = 1, col = 0;
if(col == n) {
puts("NO");
continue;
}
bool ok = true;
while(true) {
if(col != fcol) {
if(a[col + row * n] <= 2)
a[col + row * n] = 2;
else
if(frow == 0)
a[col + row * n] = 4;
else
a[col + row * n] = 5;
}
if(row != frow) {
if(a[col + row * n] <= 2)
a[col + row * n] = 1;
else
if(frow == 0)
a[col + row * n] = 6;
else
a[col + row * n] = 3;
}
trow = row, tcol = col;
if(frow == 0 && a[tcol + trow * n] == 1)
++row;
else if(frow == 1 && a[tcol + trow * n] == 1)
--row;
if(a[tcol + trow * n] == 4)
++row;
if(a[tcol + trow * n] == 2 || a[tcol + trow * n] == 3 || a[tcol + trow * n] == 6)
++col;
if(a[tcol + trow * n] == 5)
--row;
frow = trow, fcol = tcol;
if(row < 0 || row > 1) {
ok = false;
break;
}
if(col >= n)
break;
}
if(ok && col == n && row == 1)
puts("YES");
else
puts("NO");
}
return 0;
}Input
7
2323216
1615124
1
3
4
2
13
24
2
12
34
3
536
345
2
46
54
Output
YES
NO
Demonstration
Codeforcess Solution C. Pipes-Solution in C, C++, Java, Python
