Algorithm
Code Examples
#1 Code Example with C++ Programming
Code -
C++ Programming
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct lex_compare {
bool operator() (const pair<int, int>& lhs, const pair<int, int>& rhs) const {
if(lhs.second != rhs.second)
return lhs.second < rhs.second;
return lhs.first > rhs.first;
}
};
int const N = 1e5 + 1;
int n, k, a[N], fr[N];
vector<int> all;
set<pair<int, int>, lex_compare> st;
int main() {
scanf("%d %d", &n, &k);
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
scanf("%d", a + i);
all.push_back(a[i]);
}
sort(all.begin(), all.end());
all.resize(unique(all.begin(), all.end()) - all.begin());
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
a[i] = lower_bound(all.begin(), all.end(), a[i]) - all.begin();
for(int i = 0; i < k; ++i)
++fr[a[i]];
for(int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
if(fr[i] != 0)
st.insert({i, fr[i]});
int l = 0, r = k - 1;
do {
if((*st.begin()).second == 1)
printf("%d\n", all[(*st.begin()).first]);
else
puts("Nothing");
st.erase({a[l], fr[a[l]]});
--fr[a[l]];
if(fr[a[l]] != 0)
st.insert({a[l], fr[a[l]]});
++l, ++r;
if(r >= n)
break;
if(fr[a[r]] != 0)
st.erase({a[r], fr[a[r]]});
++fr[a[r]];
st.insert({a[r], fr[a[r]]});
} while(r < n);
return 0;
}Input
5 3
1
2
2
3
3
1
2
2
3
3
Output
1
3
2
3
2
Demonstration
Codeforcess Solution Subsegments, E. Subsegments C,C++, Java, Js and Python ,E. Subsegments,Codeforcess Solution

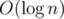 , which Sasha coped with. For Sasha not to think that he had learned all, Stas gave him a new task. For each segment of the fixed length Sasha must find the maximum element of those that occur on the given segment exactly once. Help Sasha solve this problem.
, which Sasha coped with. For Sasha not to think that he had learned all, Stas gave him a new task. For each segment of the fixed length Sasha must find the maximum element of those that occur on the given segment exactly once. Help Sasha solve this problem.