Algorithm
In mathematics, the Pythagorean theorem — is a relation in Euclidean geometry among the three sides of a right-angled triangle. In terms of areas, it states:
In any right-angled triangle, the area of the square whose side is the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the areas of the squares whose sides are the two legs (the two sides that meet at a right angle).
The theorem can be written as an equation relating the lengths of the sides a, b and c, often called the Pythagorean equation:
where c represents the length of the hypotenuse, and a and b represent the lengths of the other two sides.
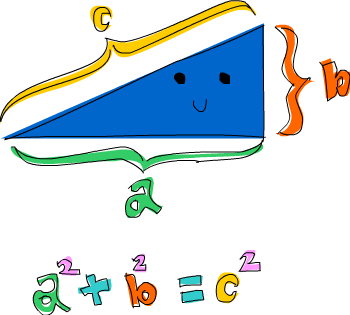
Given n, your task is to count how many right-angled triangles with side-lengths a, b and c that satisfied an inequality 1 ≤ a ≤ b ≤ c ≤ n.
The only line contains one integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 104) as we mentioned above.
Print a single integer — the answer to the problem.
5
1
74
35
Code Examples
#1 Code Example with C++ Programming
Code -
C++ Programming
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int t, counter = 0;
cin >> t;
double tmp;
for (int i = 1; i < t; i++) {
for (int j = i; (i*i) + (j*j) <= (t*t); j++) {
tmp = i*i + j*j;
if (int(sqrt(tmp)) * int(sqrt(tmp)) == tmp)
counter++;
}
}
cout << counter << endl;
return 0;
}Input
Output
Demonstration
Codeforces Solution-Pythagorean Theorem II-Solution in C, C++, Java, Python
