Algorithm
You are given a chessboard of size n×n. It is filled with numbers from 1 to n2 in the following way: the first ⌈n22⌉ numbers from 1 to ⌈n22⌉ are written in the cells with even sum of coordinates from left to right from top to bottom. The rest n2−⌈n22⌉ numbers from ⌈n22⌉+1 to n2 are written in the cells with odd sum of coordinates from left to right from top to bottom. The operation ⌈xy⌉ means division x by y rounded up.
For example, the left board on the following picture is the chessboard which is given for n=4 and the right board is the chessboard which is given for n=5.
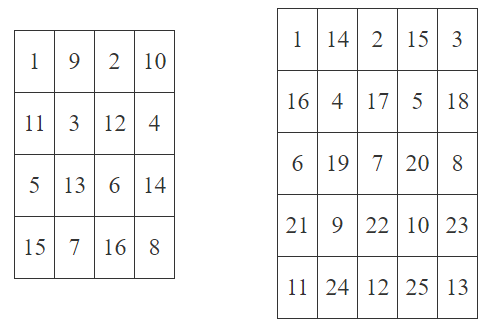
You are given q queries. The i-th query is described as a pair xi,yi. The answer to the i-th query is the number written in the cell xi,yi (xi is the row, yi is the column). Rows and columns are numbered from 1 to n.
The first line contains two integers n and q (1≤n≤109, 1≤q≤105) — the size of the board and the number of queries.
The next q lines contain two integers each. The i-th line contains two integers xi,yi (1≤xi,yi≤n) — description of the i-th query.
For each query from 1 to q print the answer to this query. The answer to the i-th query is the number written in the cell xi,yi (xi is the row, yi is the column). Rows and columns are numbered from 1 to n. Queries are numbered from 1 to q in order of the input.
4 5
1 1
4 4
4 3
3 2
2 4
1
8
16
13
4
5 4
2 1
4 2
3 3
3 4
16
9
7
20
Answers to the queries from examples are on the board in the picture from the problem statement.
Code Examples
#1 Code Example with C++ Programming
Code -
C++ Programming
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
long long n, q, x, y, o, e, oo, ee;
int main() {
scanf("%lld %lld", &n, &q);
if(n % 2 == 0)
o = e = n / 2;
else
o = n / 2 + 1, e = n / 2;
while(q-- != 0) {
scanf("%lld %lld", &x, &y);
long long bf = 0;
if((x + y) % 2 == 0)
oo = o, ee = e;
else
oo = e, ee = o;
long long xb = x - 1;
if(xb % 2 == 0)
bf = xb / 2 * oo + xb / 2 * ee;
else
bf = (xb / 2 + 1) * oo + xb / 2 * ee;
long long yb = y - 1;
bf += yb / 2;
if((x + y) % 2 == 0)
printf("%lld\n", bf + 1);
else
printf("%lld\n", ((1ll * n * n + 1) / 2) + 1 + bf);
}
return 0;
}Input
1 1
4 4
4 3
3 2
2 4
Output
8
16
13
4
Demonstration
Codeforces Solution-B. Numbers on the Chessboard-Solution in C, C++, Java, Python
