Algorithm
While Farmer John rebuilds his farm in an unfamiliar portion of Bovinia, Bessie is out trying some alternative jobs. In her new gig as a reporter, Bessie needs to know about programming competition results as quickly as possible. When she covers the 2016 Robot Rap Battle Tournament, she notices that all of the robots operate under deterministic algorithms. In particular, robot i will beat robot j if and only if robot i has a higher skill level than robot j. And if robot i beats robot j and robot j beats robot k, then robot i will beat robot k. Since rapping is such a subtle art, two robots can never have the same skill level.
Given the results of the rap battles in the order in which they were played, determine the minimum number of first rap battles that needed to take place before Bessie could order all of the robots by skill level.
The first line of the input consists of two integers, the number of robots n (2 ≤ n ≤ 100 000) and the number of rap battles m (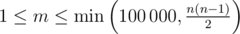 ).
).
The next m lines describe the results of the rap battles in the order they took place. Each consists of two integers ui and vi (1 ≤ ui, vi ≤ n, ui ≠ vi), indicating that robot ui beat robot vi in the i-th rap battle. No two rap battles involve the same pair of robots.
It is guaranteed that at least one ordering of the robots satisfies all m relations.
Print the minimum k such that the ordering of the robots by skill level is uniquely defined by the first k rap battles. If there exists more than one ordering that satisfies all m relations, output -1.
4 5
2 1
1 3
2 3
4 2
4 3
4
3 2
1 2
3 2
-1
In the first sample, the robots from strongest to weakest must be (4, 2, 1, 3), which Bessie can deduce after knowing the results of the first four rap battles.
In the second sample, both (1, 3, 2) and (3, 1, 2) are possible orderings of the robots from strongest to weakest after both rap battles.
Code Examples
#1 Code Example with C++ Programming
Code -
C++ Programming
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int const N = 1e5 + 1;
int n, m, in[N];
priority_queue<int> pq;
vector<pair<int, int> > edges;
vector<vector<int> > g;
bool can(int mid) {
while(!pq.empty())
pq.pop();
memset(in, 0, sizeof in);
g.clear();
g.resize(n);
for(int i = 0; i < mid; ++i) {
++in[edges[i].second];
g[edges[i].first].push_back(edges[i].second);
}
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
if(in[i] == 0) {
pq.push(i);
if(pq.size() > 1)
return false;
}
while(!pq.empty()) {
int u = pq.top();
pq.pop();
for(int i = 0; i < g[u].size(); ++i)
if(--in[g[u][i]] == 0)
pq.push(g[u][i]);
if(pq.size() > 1)
return false;
}
return true;
}
int main() {
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
for(int i = 0, a, b; i < m; ++i) {
scanf("%d %d", &a, &b);
--a, --b;
edges.push_back({a, b});
}
int l = 1, r = m, mid, res = -1;
while(l <= r) {
mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if(can(mid))
res = mid, r = mid - 1;
else
l = mid + 1;
}
printf("%d\n", res);
return 0;
}Input
2 1
1 3
2 3
4 2
4 3
Output
Demonstration
Codeforces Solution-Robot Rapping Results Report-Solution in C, C++, Java, Python
