Algorithm
Code Examples
#1 Code Example with C++ Programming
Code -
C++ Programming
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
struct chessman {
char k;
int x, y;
};
using namespace std;
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
int kx, ky;
cin >> kx >> ky;
chessman best_top;
best_top.k = ' ';
chessman best_right;
best_right.k = ' ';
chessman best_bottom;
best_bottom.k = ' ';
chessman best_left;
best_left.k = ' ';
chessman best_top_right;
best_top_right.k = ' ';
chessman best_bottom_right;
best_bottom_right.k = ' ';
chessman best_bottom_left;
best_bottom_left.k = ' ';
chessman best_top_left;
best_top_left.k = ' ';
while(n--) {
char k;
int x, y;
cin >> k >> x >> y;
if(abs(x) + abs(y) == abs(kx) + abs(ky) || abs(x) - abs(y) == abs(kx) - abs(ky)) {
if(x > kx && y > ky) {
if(best_top_right.k == ' ' || (x < best_top_right.x && y < best_top_right.y)) {
best_top_right.k = k;
best_top_right.x = x;
best_top_right.y = y;
}
} else if(x > kx && y < ky) {
if(best_bottom_right.k == ' ' || (x < best_bottom_right.x && y < best_bottom_right.y)) {
best_bottom_right.k = k;
best_bottom_right.x = x;
best_bottom_right.y = y;
}
} else if(x < kx && y < ky) {
if(best_bottom_left.k == ' ' || (x > best_bottom_left.x && y > best_bottom_left.y)) {
best_bottom_left.k = k;
best_bottom_left.x = x;
best_bottom_left.y = y;
}
} else if(x < kx && y > ky) {
if(best_top_left.k == ' ' || (x > best_top_left.x && y < best_top_left.y)) {
best_top_left.k = k;
best_top_left.x = x;
best_top_left.y = y;
}
}
} else if(x == kx) {
if(y > ky) {
if(best_top.k == ' ' || y < best_top.y) {
best_top.k = k;
best_top.x = x;
best_top.y = y;
}
} else if(y < ky) {
if(best_bottom.k == ' ' || y > best_bottom.y) {
best_bottom.k = k;
best_bottom.x = x;
best_bottom.y = y;
}
}
} else if(y == ky) {
if(x > kx) {
if(best_right.k == ' ' || x < best_right.x) {
best_right.k = k;
best_right.x = x;
best_right.y = y;
}
} else if(x < kx) {
if(best_left.k == ' ' || x > best_left.x) {
best_left.k = k;
best_left.x = x;
best_left.y = y;
}
}
}
}
if(best_top.k == 'Q' || best_top.k == 'R' ||
best_right.k == 'Q' || best_right.k == 'R' ||
best_bottom.k == 'Q' || best_bottom.k == 'R' ||
best_left.k == 'Q' || best_left.k == 'R' ||
best_top_right.k == 'Q' || best_top_right.k == 'B' ||
best_bottom_right.k == 'Q' || best_bottom_right.k == 'B' ||
best_bottom_left.k == 'Q' || best_bottom_left.k == 'B' ||
best_top_left.k == 'Q' || best_top_left.k == 'B') {
cout << "YES" << endl;
} else {
cout << "NO" << endl;
}
return 0;
}Input
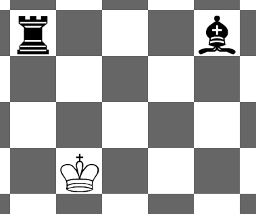
2
4 2
R 1 1
B 1 5
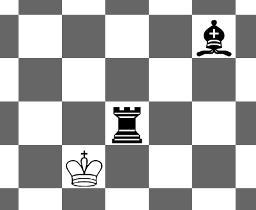
4 2
R 1 1
B 1 5
Output
YES
Demonstration
Codeforces Solution-Anton and Chess-Solution in C, C++, Java, Python