Algorithm
Problem Name: 1020. Number of Enclaves
You are given an m x n binary matrix grid, where 0 represents a sea cell and 1 represents a land cell.
A move consists of walking from one land cell to another adjacent (4-directionally) land cell or walking off the boundary of the grid.
Return the number of land cells in grid for which we cannot walk off the boundary of the grid in any number of moves.
Example 1:
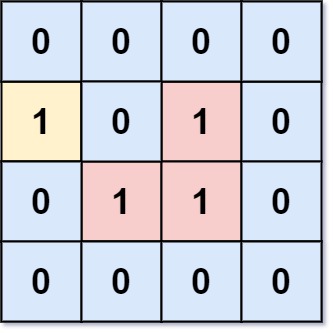
Input: grid = [[0,0,0,0],[1,0,1,0],[0,1,1,0],[0,0,0,0]] Output: 3 Explanation: There are three 1s that are enclosed by 0s, and one 1 that is not enclosed because its on the boundary.
Example 2:
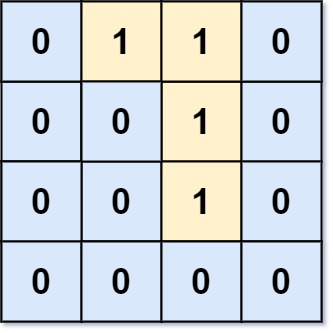
Input: grid = [[0,1,1,0],[0,0,1,0],[0,0,1,0],[0,0,0,0]] Output: 0 Explanation: All 1s are either on the boundary or can reach the boundary.
Constraints:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 500grid[i][j]is either0or1.
Code Examples
#1 Code Example with Java Programming
Code -
Java Programming
class Solution {
private static final int[][] DIRS = {{1, 0}, {0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {0, -1}};
public int numEnclaves(int[][] grid) {
Queue < int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();
int result = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < grid.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < grid[0].length; j++) {
result += grid[i][j];
if (i * j == 0 || i == grid.length - 1 || j == grid[i].length - 1) {
queue.add(new int[]{i, j});
}
}
}
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int[] removed = queue.remove();
int x = removed[0];
int y = removed[1];
if (x < 0 || y < 0 || x == grid.length || y == grid[0].length || grid[x][y] != 1) {
continue;
}
grid[x][y] = 0;
result--;
for (int[] dir : DIRS) {
queue.add(new int[]{x + dir[0], y + dir[1]});
}
}
return result;
}
}
Input
Output
#2 Code Example with Javascript Programming
Code -
Javascript Programming
const numEnclaves = function(A) {
let res = 0
const dirs = [[-1, 0], [1, 0], [0, 1], [0, -1]]
const visited = Array.from({ length: A.length }, () =>
new Array(A[0].length).fill(false)
)
for (let row = 0; row < A.length; row++) {
for (let col = 0; A[0] && col < A[0].length; col++) {
if (
(row === 0 ||
col === 0 ||
row === A.length - 1 ||
col === A[0].length - 1) &&
A[row][col] === 1
) {
dfs(A, row, col, visited, dirs)
}
}
}
for (let row = 0; row < A.length; row++) {
for (let col = 0; A[0] && col < A[0].length; col++) {
if (A[row][col] === 1) {
res += 1
}
}
}
return res
}
function dfs(A, row, col, v, dirs) {
if (
row < 0 ||
row >= A.length ||
col < 0 ||
col >= A[0].length ||
v[row][col] ||
A[row][col] === 0
)
return
v[row][col] = true
A[row][col] = 0
for (let dir of dirs) {
dfs(A, row + dir[0], col + dir[1], v, dirs)
}
}
Input
Output
#3 Code Example with Python Programming
Code -
Python Programming
class Solution:
def numEnclaves(self, A: List[List[int]]) -> int:
def dfs(i, j):
A[i][j] = 0
for x, y in (i - 1, j), (i + 1, j), (i, j - 1), (i, j + 1):
if 0 <= x < m and 0 <= y < n and A[x][y]:
dfs(x, y)
m, n = len(A), len(A[0])
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
if A[i][j] == 1 and (i == 0 or j == 0 or i == m - 1 or j == n - 1):
dfs(i, j)
return sum(sum(row) for row in A)
Input
