Algorithm
Problem Name: 257. Binary Tree Paths
Given the root of a binary tree, return all root-to-leaf paths in any order.
A leaf is a node with no children.
Example 1:
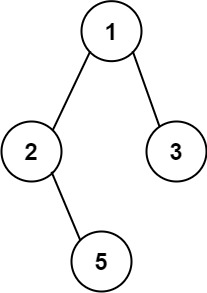
Input: root = [1,2,3,null,5] Output: ["1->2->5","1->3"]
Example 2:
Input: root = [1] Output: ["1"]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 100]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
Code Examples
#1 Code Example with C Programming
Code -
C Programming
typedef struct {
char *b;
int sz;
int n;
} buff_t;
void buff_int(buff_t *buff, int k) {
int l;
if (buff->n + 10 + 2 + 1 >= buff->sz) {
buff->sz *= 2;
buff->sz += 10 + 2 + 1;
buff->b = realloc(buff->b, buff->sz * sizeof(char));
//assert(buff->b);
}
l = sprintf(&buff->b[buff->n], "%d", k);
buff->n += l;
}
void buff_str(buff_t *buff, char *s, int len) {
strcpy(&buff->b[buff->n], s);
buff->n += len;
}
typedef struct {
char **p;
int sz;
int n;
} res_t;
void add2res(res_t *res, char *s) {
if (res->sz == res->n) {
res->sz *= 2;
res->p = realloc(res->p, res->sz * sizeof(char *));
//assert(res->p);
}
res->p[res->n ++] = s;
}
void travesal(struct TreeNode *node, buff_t *buff, int n, res_t *res) {
if (!node) return;
buff->n = n;
buff_int(buff, node->val);
if (!node->left && !node->right) {
add2res(res, strdup(buff->b));
return;
}
buff_str(buff, "->", 2);
n = buff->n; // tricky, save it for next recursion, it always starts from here.
travesal(node->left, buff, n, res);
travesal(node->right, buff, n, res);
}
char** binaryTreePaths(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize) {
res_t res;
buff_t buff;
*returnSize = 0;
res.n = 0;
res.sz = 100;
res.p = malloc(res.sz * sizeof(char *));
//assert(res.p);
buff.n = 0;
buff.sz = 100;
buff.b = malloc(buff.sz * sizeof(char));
//assert(buff.b);
travesal(root, &buff, 0, &res);
free(buff.b);
*returnSize = res.n;
return res.p;
}
Input
Output
#2 Code Example with C++ Programming
Code -
C++ Programming
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode* root) {
vector<string>res;
if(!root) return res;
DFS(root, res, "");
return res;
}
void DFS(TreeNode* root, vector < string>& res, string path){
path += to_string(root->val);
if(root->left || root->right) path += "->";
else{
res.push_back(path);
return;
}
if(root->left) DFS(root->left, res, path);
if(root->right) DFS(root->right, res, path);
}
};
Input
Output
#3 Code Example with Java Programming
Code -
Java Programming
class Solution {
public List binaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) {
List result = new ArrayList<>();
helper(root, result, new StringBuilder());
return result;
}
private void helper(TreeNode root, List < String> result, StringBuilder path) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
path.append(root.val);
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
result.add(path.toString());
} else {
path.append("->");
helper(root.left, result, new StringBuilder(path));
helper(root.right, result, new StringBuilder(path));
}
}
}
Input
Output
#4 Code Example with Javascript Programming
Code -
Javascript Programming
const binaryTreePaths = function(root) {
const res = [];
traverse(root, res, []);
return res;
};
function traverse(node, res, p) {
if (node === null) return;
p.push(node.val);
if (node.left === null && node.right === null) {
res.push(p.join("->"));
}
if (node.left) {
traverse(node.left, res, p.slice(0));
}
if (node.right) {
traverse(node.right, res, p.slice(0));
}
}
Input
Output
#5 Code Example with Python Programming
Code -
Python Programming
class Solution:
def binaryTreePaths(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[str]:
def dfs(node, arr):
if not node.right and not node.left:
#print(arr)
self.res += ['->'.join(str(num) for num in arr)]
if node.left:
dfs(node.left, arr + [node.left.val])
if node.right:
dfs(node.right, arr + [node.right.val])
self.res = []
if not root: return []
dfs(root, [root.val])
return self.res
Input
#6 Code Example with C# Programming
Code -
C# Programming
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
namespace LeetCode
{
public class _0257_BinaryTreePaths
{
public IList < string> BinaryTreePaths(TreeNode root)
{
if (root == null) return new List();
var result = new List(), result);
return result.Select(i => string.Join("->", i)).ToList();
}
public void GetPath(TreeNode node, IList < int> current, IList(current);
if (node == null) return;
next.Add(node.val);
if (node.left == null && node.right == null)
result.Add(next);
else
{
GetPath(node.left, next, result);
GetPath(node.right, next, result);
}
}
}
}
Input
Output
