Algorithm
Problem Nmae: 109. Convert Sorted List to Binary Search Tree
Given the head of a singly linked list where elements are sorted in ascending order, convert it to a
Example 1:
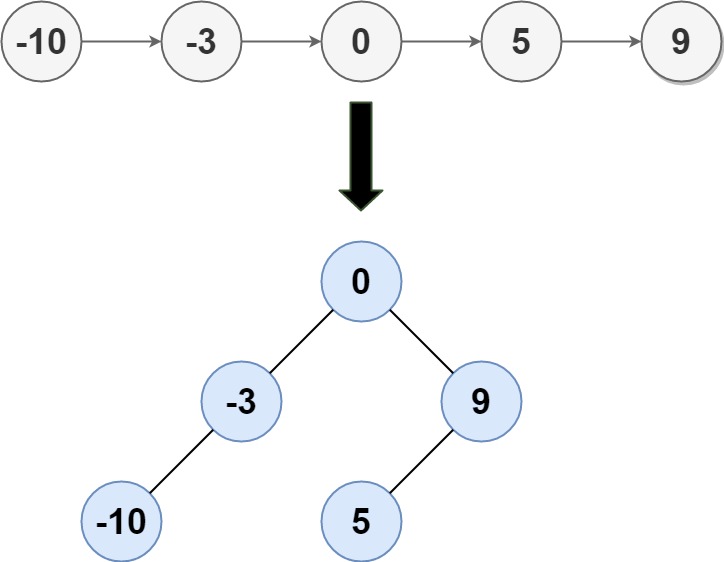
Input: head = [-10,-3,0,5,9] Output: [0,-3,9,-10,null,5] Explanation: One possible answer is [0,-3,9,-10,null,5], which represents the shown height balanced BST.
Example 2:
Input: head = [] Output: []
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in
headis in the range[0, 2 * 104]. -105 <= Node.val <= 105
Code Examples
#1 Code Example with C++ Programming
Code -
C++ Programming
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* sortedListToBST(ListNode* head) {
if(!head) return NULL;
if(!head->next) return new TreeNode(head->val);
ListNode* slow = head;
ListNode* fast = head->next;
ListNode* pre = new ListNode(0);
pre->next = slow;
// Root is the mid position of the linked list
while(fast){
slow = slow->next;
pre = pre->next;
fast = fast->next ? fast->next->next : NULL;
}
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(slow->val);
pre->next = NULL;
// Call recursively to left and right part of linked list
root->left = sortedListToBST(head);
root->right = sortedListToBST(slow->next);
return root;
}
};
Input
Output
#2 Code Example with Java Programming
Code -
Java Programming
class Solution {
ListNode curr;
public TreeNode sortedListToBST(ListNode head) {
curr = head;
return generate(count(head));
}
public int count(ListNode node) {
int n = 0;
while (node != null) {
node = node.next;
++n;
}
return n;
}
public TreeNode generate(int n) {
if (n==0) return null;
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(0);
node.left = generate(n/2);
node.val = curr.val;
curr = curr.next;
node.right = generate(n-(n/2)-1);
return node;
}
}
Input
Output
#3 Code Example with Javascript Programming
Code -
Javascript Programming
const sortedListToBST = function(head) {
if(head == null) return null
const arr = []
let cur = head
while(cur !== null) {
arr.push(cur)
cur = cur.next
}
return build(arr, null, '')
};
function build(arr, parent, type) {
if(arr.length === 0) return
let mid = Math.floor(arr.length / 2)
let left = arr.slice(0, mid)
let right = arr.slice(mid + 1)
const node = new TreeNode(arr[mid].val)
if(parent) parent[type] = node
build(left, node, 'left')
build(right, node, 'right')
return node
}
Input
Output
#4 Code Example with Python Programming
Code -
Python Programming
class Solution:
def sortedListToBST(self, head):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:rtype: TreeNode
"""
def traverse(arr):
if arr == []: return
node = TreeNode(arr[len(arr)//2])
node.left = traverse(arr[:len(arr)//2])
node.right = traverse(arr[len(arr)//2+1:])
return node
array = []
while head: array.append(head.val); head = head.next
return traverse(array)
Input
Output
#5 Code Example with C# Programming
Code -
C# Programming
namespace LeetCode
{
public class _109_ConvertSortedListToBinarySearchTree
{
private ListNode head = null;
public TreeNode SortedListToBST(ListNode head)
{
var p = head;
var length = 0;
while (p != null)
{
p = p.next;
length++;
}
this.head = head;
return SortedListToBST(0, length);
}
public TreeNode SortedListToBST(int l, int r)
{
if (l >= r) return null;
var mid = l + (r - l) / 2;
var left = SortedListToBST(l, mid);
var node = new TreeNode(head.val);
node.left = left;
this.head = this.head.next;
node.right = SortedListToBST(mid + 1, r);
return node;
}
}
}
Input
Output
