Algorithm
Problem Name: 688. Knight Probability in Chessboard
On an n x n chessboard, a knight starts at the cell (row, column) and attempts to make exactly k moves. The rows and columns are 0-indexed, so the top-left cell is (0, 0), and the bottom-right cell is (n - 1, n - 1).
A chess knight has eight possible moves it can make, as illustrated below. Each move is two cells in a cardinal direction, then one cell in an orthogonal direction.
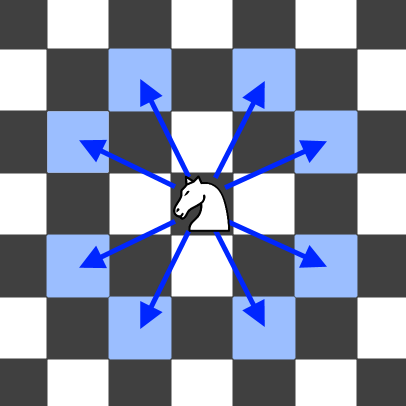
Each time the knight is to move, it chooses one of eight possible moves uniformly at random (even if the piece would go off the chessboard) and moves there.
The knight continues moving until it has made exactly k moves or has moved off the chessboard.
Return the probability that the knight remains on the board after it has stopped moving.
Example 1:
Input: n = 3, k = 2, row = 0, column = 0 Output: 0.06250 Explanation: There are two moves (to (1,2), (2,1)) that will keep the knight on the board. From each of those positions, there are also two moves that will keep the knight on the board. The total probability the knight stays on the board is 0.0625.
Example 2:
Input: n = 1, k = 0, row = 0, column = 0 Output: 1.00000
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 250 <= k <= 1000 <= row, column <= n - 1
Code Examples
#1 Code Example with C++ Programming
Code -
C++ Programming
class Solution {
private:
unordered_map<int, unordered_map<int, unordered_map<int, double>>>dp;
public:
double knightProbability(int N, int K, int r, int c) {
if(dp.count(r) && dp[r].count(c) && dp[r][c].count(K)) return dp[r][c][K];
if(r < 0 || r >= N || c < 0 || c >= N) return 0;
if(K == 0) return 1;
double total = knightProbability(N, K - 1, r - 1, c - 2) + knightProbability(N, K - 1, r - 2, c - 1)
+ knightProbability(N, K - 1, r - 1, c + 2) + knightProbability(N, K - 1, r - 2, c + 1)
+ knightProbability(N, K - 1, r + 1, c + 2) + knightProbability(N, K - 1, r + 2, c + 1)
+ knightProbability(N, K - 1, r + 1, c - 2) + knightProbability(N, K - 1, r + 2, c - 1);
double res = total / 8;
dp[r][c][K] = res;
return res;
}
};
Input
Output
#2 Code Example with Java Programming
Code -
Java Programming
class Solution {
public double knightProbability(int N, int K, int r, int c) {
double[][] dp = new double[N][N];
int[] rowMoves = new int[]{2, 2, 1, 1, -1, -1, -2, -2};
int[] colMoves = new int[]{1, -1, 2, -2, 2, -2, 1, -1};
dp[r][c] = 1;
while (K-- > 0) {
double[][] copy = new double[N][N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < 8; k++) {
int destR = i + rowMoves[k];
int destC = j + colMoves[k];
if (destR >= 0 && destR < N && destC >= 0 && destC < N) {
copy[destR][destC] += dp[i][j] / 8.0;
}
}
}
}
dp = copy;
}
double ans = 0.0;
for (double[] row : dp) {
for (double val : row) {
ans += val;
}
}
return ans;
}
}
Input
Output
#3 Code Example with Javascript Programming
Code -
Javascript Programming
const knightProbability = function (N, K, r, c) {
const moves = [
[1, 2],
[1, -2],
[2, 1],
[2, -1],
[-1, 2],
[-1, -2],
[-2, 1],
[-2, -1],
]
const dp = [...Array(K + 1)].map(() =>
[...Array(N)].map(() => Array(N).fill(0))
)
dp[0][r][c] = 1
for (let step = 1; step < = K; step++) {
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < N; j++) {
for (let move of moves) {
let row = i + move[0],
col = j + move[1]
if (row >= 0 && row < N && col >= 0 && col < N)
dp[step][i][j] += dp[step - 1][row][col] / 8
}
}
}
}
let res = 0
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < N; j++) {
res += dp[K][i][j]
}
}
return res
}
Input
Output
#4 Code Example with Python Programming
Code -
Python Programming
class Solution:
def knightProbability(self, N, K, r, c):
memo = {}
def dfs(i, j, p, k):
if 0 <= i < N and 0 <= j < N and k < K:
sm = 0
for x, y in ((-1, -2), (-2, -1), (-2, 1), (-1, 2), (1, 2), (2, 1), (2, -1), (1, -2)):
if (i + x, j + y, k) not in memo:
memo[(i + x, j + y, k)] = dfs(i + x, j + y, p / 8, k + 1)
sm += memo[(i + x, j + y, k)]
return sm
else:
return 0 <= i < N and 0 <= j < N and p or 0
return dfs(r, c, 1, 0)
Input
Output
