Algorithm
Problem Name: 872. Leaf-Similar Trees
Consider all the leaves of a binary tree, from left to right order, the values of those leaves form a leaf value sequence.
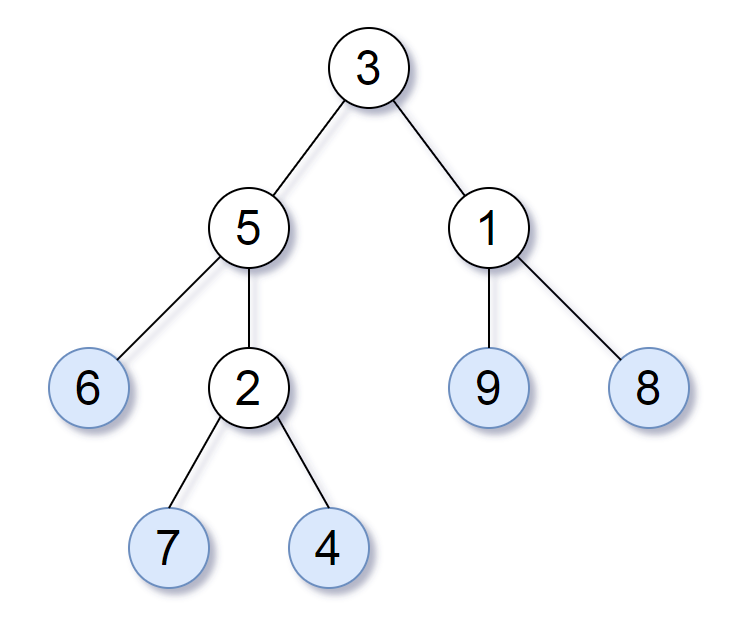
For example, in the given tree above, the leaf value sequence is (6, 7, 4, 9, 8).
Two binary trees are considered leaf-similar if their leaf value sequence is the same.
Return true if and only if the two given trees with head nodes root1 and root2 are leaf-similar.
Example 1:
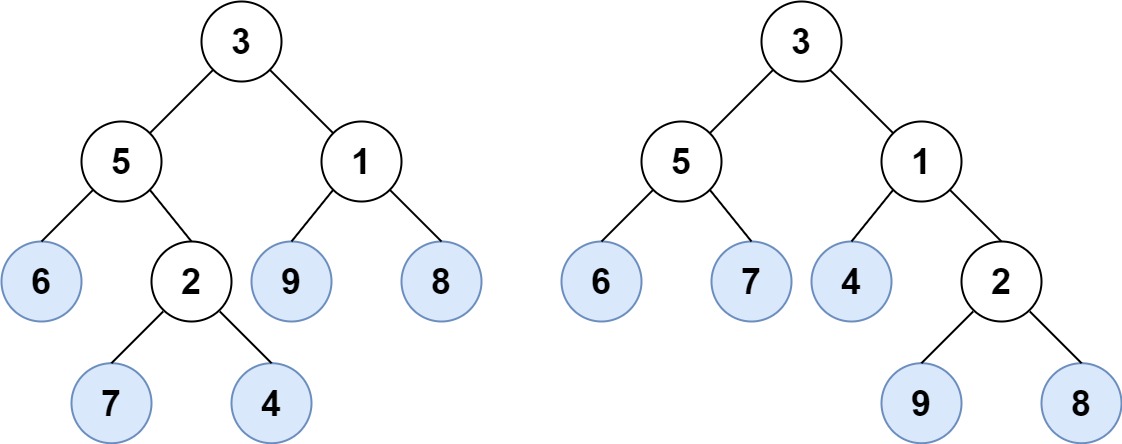
Input: root1 = [3,5,1,6,2,9,8,null,null,7,4], root2 = [3,5,1,6,7,4,2,null,null,null,null,null,null,9,8] Output: true
Example 2:
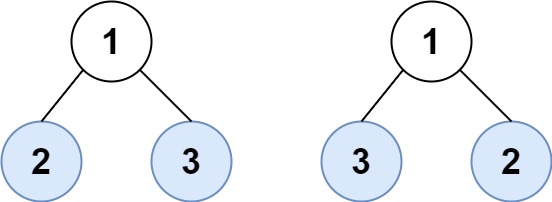
Input: root1 = [1,2,3], root2 = [1,3,2] Output: false
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in each tree will be in the range
[1, 200]. - Both of the given trees will have values in the range
[0, 200].
Code Examples
#1 Code Example with C++ Programming
Code -
C++ Programming
class Solution {
public:
bool leafSimilar(TreeNode* root1, TreeNode* root2) {
vector<int>v;
int pos = 0;
dfs(root1, v, pos);
pos = 0;
return dfs(root2, v, pos);
}
bool dfs(TreeNode* p, vector<int>& v, int& pos){
if(!p) return true;
if(!p->left && !p->right){
if(v.size() == pos) v.push_back(p->val);
return v[pos++] == p->val;
}
return dfs(p->left, v, pos) && dfs(p->right, v, pos);
}
};
Input
Output
#2 Code Example with Java Programming
Code -
Java Programming
class Solution {
public boolean leafSimilar(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) {
StringBuilder leavesOne = new StringBuilder();
StringBuilder leavesTwo = new StringBuilder();
populateLeaves(root1, leavesOne);
populateLeaves(root2, leavesTwo);
return leavesOne.toString().equals(leavesTwo.toString());
}
private void populateLeaves(TreeNode root, StringBuilder leaves) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
leaves.append(root.val).append(",");
return;
}
populateLeaves(root.left, leaves);
populateLeaves(root.right, leaves);
}
}
Input
Output
#3 Code Example with Python Programming
Code -
Python Programming
class Solution:
def leafSimilar(self, root1, root2):
def dfs(node, arr):
if node:
if not node.left and not node.right: arr += [node.val]
dfs(node.left, arr)
dfs(node.right, arr)
return arr
return dfs(root1, []) == dfs(root2, [])
Input
Output
#4 Code Example with C# Programming
Code -
C# Programming
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
namespace LeetCode
{
public class _0872_LeafSimilarTrees
{
public bool LeafSimilar(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2)
{
var leaves1 = new List < int>();
var leaves2 = new List<int>();
InOrder(root1, leaves1);
InOrder(root2, leaves2);
return leaves1.SequenceEqual(leaves2);
}
private void InOrder(TreeNode node, IList < int> leaves)
{
if (node == null) return;
if (node.left == null && node.right == null)
{
leaves.Add(node.val);
return;
}
InOrder(node.left, leaves);
InOrder(node.right, leaves);
}
}
}
Input
Output
