Algorithm
Problem Name: 1022. Sum of Root To Leaf Binary Numbers
You are given the root of a binary tree where each node has a value 0 or 1. Each root-to-leaf path represents a binary number starting with the most significant bit.
- For example, if the path is
0 -> 1 -> 1 -> 0 -> 1, then this could represent01101in binary, which is13.
For all leaves in the tree, consider the numbers represented by the path from the root to that leaf. Return the sum of these numbers.
The test cases are generated so that the answer fits in a 32-bits integer.
Example 1:
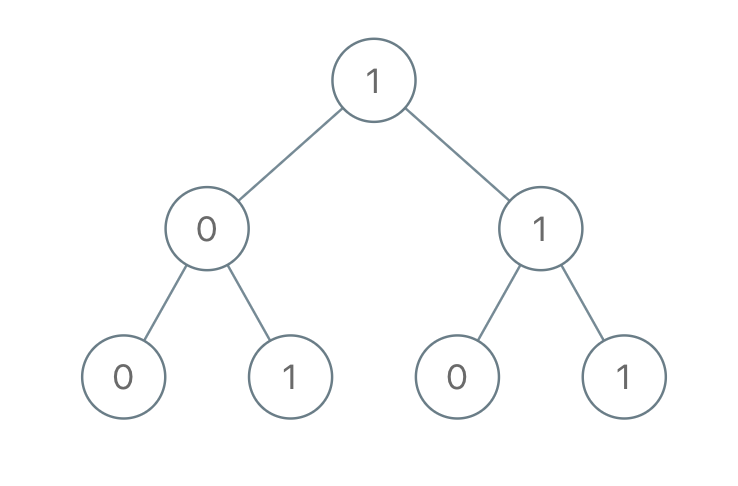
Input: root = [1,0,1,0,1,0,1] Output: 22 Explanation: (100) + (101) + (110) + (111) = 4 + 5 + 6 + 7 = 22
Example 2:
Input: root = [0] Output: 0
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 1000]. Node.valis0or1.
Code Examples
#1 Code Example with Java Programming
Code -
Java Programming
class Solution {
public int sumRootToLeaf(TreeNode root) {
Queue queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(new NodeToBinaryRepresentation(root, new StringBuilder()));
int sum = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
while (size-- > 0) {
NodeToBinaryRepresentation removed = queue.remove();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder().append(removed.sb.toString()).append(removed.node.val);
if (removed.node.left == null && removed.node.right == null) {
sum += getIntegerValue(sb.toString());
} else {
if (removed.node.left != null) {
queue.add(new NodeToBinaryRepresentation(removed.node.left, sb));
}
if (removed.node.right != null) {
queue.add(new NodeToBinaryRepresentation(removed.node.right, sb));
}
}
}
}
return sum;
}
private int getIntegerValue(String s) {
int value = 0;
int multiplier = 1;
for (int i = s.length() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
value += Character.getNumericValue(s.charAt(i)) * multiplier;
multiplier *= 2;
}
return value;
}
private static class NodeToBinaryRepresentation {
TreeNode node;
StringBuilder sb;
public NodeToBinaryRepresentation(TreeNode node, StringBuilder sb) {
this.node = node;
this.sb = sb;
}
}
}
Input
Output
#2 Code Example with Javascript Programming
Code -
Javascript Programming
const sumRootToLeaf = function(root) {
if(root == null) return 0
const res = []
dfs(root, 0, res)
const mod = Math.pow(10, 9) + 7
return res.reduce((ac, el) => (ac + el) % mod ,0)
};
function dfs(node, val, res) {
const mod = Math.pow(10, 9) + 7
if(node == null) return
val = (val * 2 + node.val) % mod
if(node.left === null && node.right === null) {
res.push(val)
}
dfs(node.left, val, res)
dfs(node.right, val, res)
}
Input
Output
#3 Code Example with Python Programming
Code -
Python Programming
class Solution:
def sumRootToLeaf(self, r: TreeNode, num = 0) -> int:
if not r:
return 0
num = (num << 1) + r.val
return (self.sumRootToLeaf(r.left, num) + self.sumRootToLeaf(r.right, num) if r.left or r.right else num) % (10 ** 9 + 7)
Input
#4 Code Example with C# Programming
Code -
C# Programming
namespace LeetCode
{
public class _1022_SumOfRootToLeafBinaryNumbers
{
public int SumRootToLeaf(TreeNode root)
{
var sum = 0;
Helper(root, 0, ref sum);
return sum;
}
private void Helper(TreeNode node, int current, ref int sum)
{
if (node == null) return;
current = current * 2 + node.val;
if (node.left == null && node.right == null)
{
sum += current;
return;
}
Helper(node.left, current, ref sum);
Helper(node.right, current, ref sum);
}
}
}
Input
