Algorithm
Problem Name: 623. Add One Row to Tree
Given the root of a binary tree and two integers val and depth, add a row of nodes with value val at the given depth depth.
Note that the root node is at depth 1.
The adding rule is:
- Given the integer
depth, for each not null tree nodecurat the depthdepth - 1, create two tree nodes with valuevalascur's left subtree root and right subtree root. cur's original left subtree should be the left subtree of the new left subtree root.cur's original right subtree should be the right subtree of the new right subtree root.- If
depth == 1that means there is no depthdepth - 1at all, then create a tree node with valuevalas the new root of the whole original tree, and the original tree is the new root's left subtree.
Example 1:
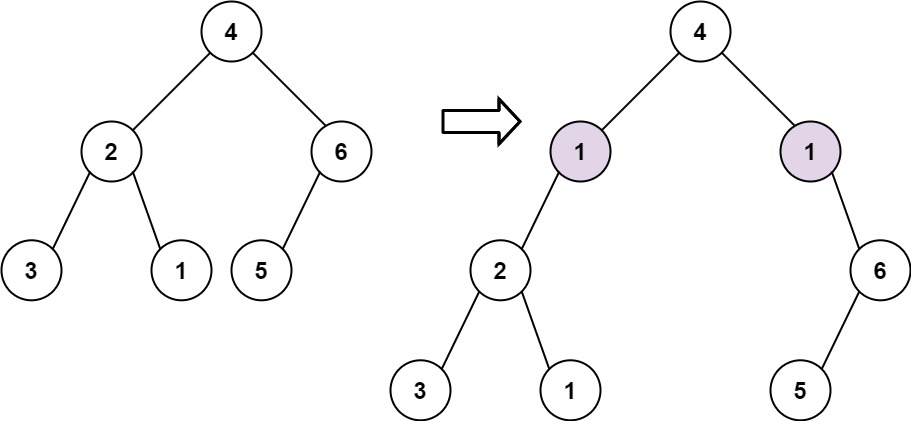
Input: root = [4,2,6,3,1,5], val = 1, depth = 2 Output: [4,1,1,2,null,null,6,3,1,5]
Example 2:
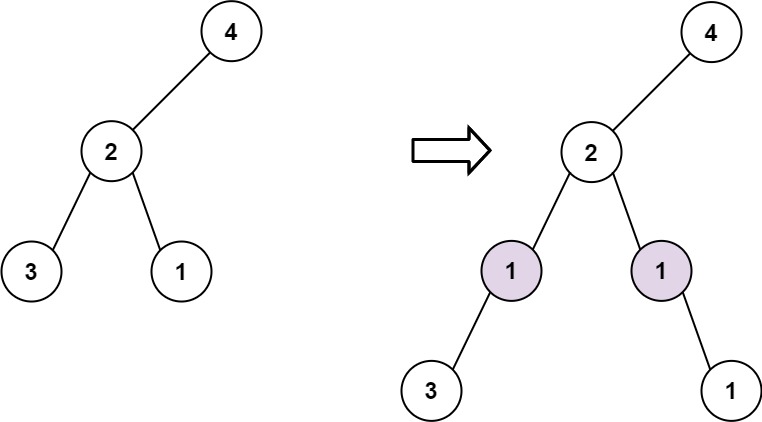
Input: root = [4,2,null,3,1], val = 1, depth = 3 Output: [4,2,null,1,1,3,null,null,1]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 104]. - The depth of the tree is in the range
[1, 104]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100-105 <= val <= 1051 <= depth <= the depth of tree + 1
Code Examples
#1 Code Example with Java Programming
Code -
Java Programming
class Solution {
public TreeNode addOneRow(TreeNode root, int val, int depth) {
if (depth == 1) {
TreeNode newRoot = new TreeNode(val);
newRoot.left = root;
return newRoot;
}
int currDepth = 1;
Queue < TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while (currDepth < depth - 1) {
Queue temp = new LinkedList<>();
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode removed = queue.remove();
if (removed.left != null) {
temp.add(removed.left);
}
if (removed.right != null) {
temp.add(removed.right);
}
}
queue = temp;
currDepth++;
}
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = queue.remove();
TreeNode temp = node.left;
node.left = new TreeNode(val);
node.left.left = temp;
temp = node.right;
node.right = new TreeNode(val);
node.right.right = temp;
}
return root;
}
}
Input
Output
#2 Code Example with Javascript Programming
Code -
Javascript Programming
const addOneRow = function (root, v, d, level = 1) {
if (d === 1) {
const node = new TreeNode(v)
node.left = root
return node
}
const queue = []
queue.push(root)
let depth = 1
while (queue.length) {
const size = queue.length
for (let i = 0; i < size; i++) {
const cur = queue.shift()
if (depth === d - 1) {
let left = new TreeNode(v)
let right = new TreeNode(v)
left.left = cur.left
right.right = cur.right
cur.left = left
cur.right = right
} else {
if (cur.left !== null) {
queue.push(cur.left)
}
if (cur.right !== null) {
queue.push(cur.right)
}
}
}
depth++
}
return root
}
Input
Output
#3 Code Example with Python Programming
Code -
Python Programming
class Solution:
def addOneRow(self, root, v, d):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:type v: int
:type d: int
:rtype: TreeNode
"""
q, depth = [root], 1
while depth != d: parent, q, depth = q, [kid for node in q for kid in (node.left, node.right) if kid], depth+1
if d != 1:
for node in parent: node.left, node.right, node.left.left, node.right.right = TreeNode(v), TreeNode(v), node.left, node.right
return root
else:
first, first.left = TreeNode(v), root
return first
Input
Output
