Algorithm
Problem Name: 388. Longest Absolute File Path
Suppose we have a file system that stores both files and directories. An example of one system is represented in the following picture:
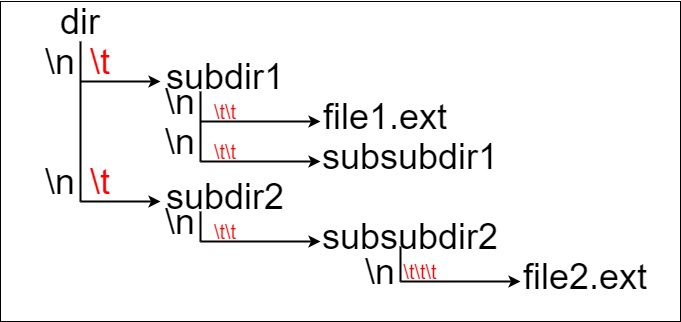
Here, we have dir as the only directory in the root. dir contains two subdirectories, subdir1 and subdir2. subdir1 contains a file file1.ext and subdirectory subsubdir1. subdir2 contains a subdirectory subsubdir2, which contains a file file2.ext.
In text form, it looks like this (with ⟶ representing the tab character):
dir ⟶ subdir1 ⟶ ⟶ file1.ext ⟶ ⟶ subsubdir1 ⟶ subdir2 ⟶ ⟶ subsubdir2 ⟶ ⟶ ⟶ file2.ext
If we were to write this representation in code, it will look like this: "dir\n\tsubdir1\n\t\tfile1.ext\n\t\tsubsubdir1\n\tsubdir2\n\t\tsubsubdir2\n\t\t\tfile2.ext". Note that the '\n' and '\t' are the new-line and tab characters.
Every file and directory has a unique absolute path in the file system, which is the order of directories that must be opened to reach the file/directory itself, all concatenated by '/'s. Using the above example, the absolute path to file2.ext is "dir/subdir2/subsubdir2/file2.ext". Each directory name consists of letters, digits, and/or spaces. Each file name is of the form name.extension, where name and extension consist of letters, digits, and/or spaces.
Given a string input representing the file system in the explained format, return the length of the longest absolute path to a file in the abstracted file system. If there is no file in the system, return 0.
Note that the testcases are generated such that the file system is valid and no file or directory name has length 0.
Example 1:
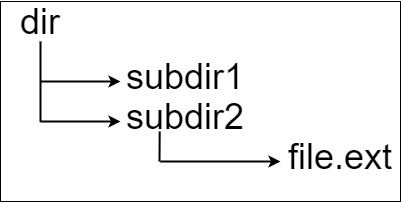
Input: input = "dir\n\tsubdir1\n\tsubdir2\n\t\tfile.ext" Output: 20 Explanation: We have only one file, and the absolute path is "dir/subdir2/file.ext" of length 20.
Example 2:
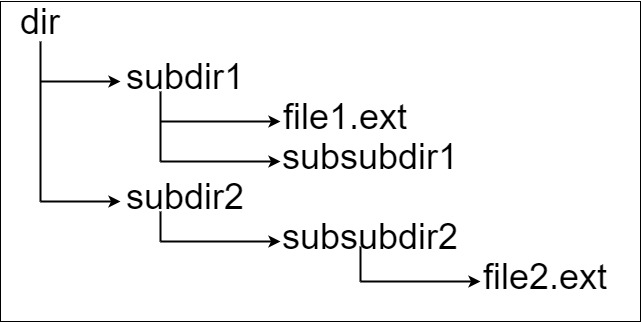
Input: input = "dir\n\tsubdir1\n\t\tfile1.ext\n\t\tsubsubdir1\n\tsubdir2\n\t\tsubsubdir2\n\t\t\tfile2.ext" Output: 32 Explanation: We have two files: "dir/subdir1/file1.ext" of length 21 "dir/subdir2/subsubdir2/file2.ext" of length 32. We return 32 since it is the longest absolute path to a file.
Example 3:
Input: input = "a" Output: 0 Explanation: We do not have any files, just a single directory named "a".
Constraints:
1 <= input.length <= 104inputmay contain lowercase or uppercase English letters, a new line character'\n', a tab character'\t', a dot'.', a space' ', and digits.- All file and directory names have positive length.
Code Examples
#1 Code Example with C Programming
Code -
C Programming
int lengthLongestPath(char* input) {
int stack[100];
int sz = 100, sp = 0;
int l = 0, n = 0;
int isfile = 0, nextline = 1;
int max = 0;
if (!input) return 0;
stack[0] = 0;
while (*input) {
while (*input == '\t') {
n++; input ++;
}
while (*input && *input != '\n') {
if (*input == '.') isfile = 1;
l++; input ++;
}
if (isfile) {
l += stack[n];
max = max < l ? l : max;
isfile = 0;
} else {
l ++; // slash
stack[n + 1] = stack[n] + l;
}
n = 0; l = 0;
input ++;
}
//if (isfile && max < l) {
// max = l;
//}
return max;
}
Input
Output
#2 Code Example with Java Programming
Code -
Java Programming
class Solution {
public int lengthLongestPath(String input) {
int maxLen = 0;
int currLevel = 1;
boolean isFile = false;
int currLen = 0;
Map < Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(0, 0);
int idx = 0;
int n = input.length();
while (idx < n) {
while (idx < n && input.charAt(idx) == '\t') {
idx++;
currLevel++;
}
while (idx < n && input.charAt(idx) != '\n') {
if (input.charAt(idx) == '.') {
isFile = true;
}
currLen++;
idx++;
}
if (isFile) {
maxLen = Math.max(maxLen, map.get(currLevel - 1) + currLen);
}
else {
map.put(currLevel, map.get(currLevel - 1) + 1 + currLen);
}
currLen = 0;
currLevel = 1;
isFile = false;
idx++;
}
return maxLen;
}
}
Input
Output
#3 Code Example with Javascript Programming
Code -
Javascript Programming
const lengthLongestPath = function(input) {
const stack = []
return input.split('\n').reduce((max, p) => {
const level = p.lastIndexOf('\t') + 1
stack[level] = p.length - level + (level ? stack[level - 1] : 0)
return p.indexOf('.') === -1 ? max : Math.max(max, stack[level] + level)
}, 0)
}
Input
Output
#4 Code Example with Python Programming
Code -
Python Programming
class Solution:
def lengthLongestPath(self, input: str) -> int:
maxlen = 0
pathlen = {0: 0}
for line in input.splitlines():
name = line.lstrip('\u005Ct')
depth = len(line) - len(name)
if '.' in name:
maxlen = max(maxlen, pathlen[depth] + len(name))
else:
pathlen[depth + 1] = pathlen[depth] + len(name) + 1
return maxlen
Input
Output
