Algorithm
Problem Name: 684. Redundant Connection
In this problem, a tree is an undirected graph that is connected and has no cycles.
You are given a graph that started as a tree with n nodes labeled from 1 to n, with one additional edge added. The added edge has two different vertices chosen from 1 to n, and was not an edge that already existed. The graph is represented as an array edges of length n where edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ai and bi in the graph.
Return an edge that can be removed so that the resulting graph is a tree of n nodes. If there are multiple answers, return the answer that occurs last in the input.
Example 1:
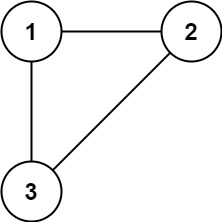
Input: edges = [[1,2],[1,3],[2,3]] Output: [2,3]
Example 2:
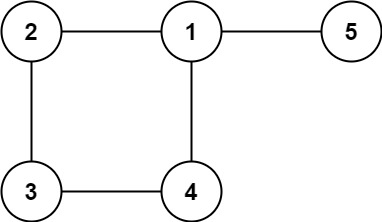
Input: edges = [[1,2],[2,3],[3,4],[1,4],[1,5]] Output: [1,4]
Constraints:
n == edges.length3 <= n <= 1000edges[i].length == 21 <= ai < bi <= edges.lengthai != bi- There are no repeated edges.
- The given graph is connected.
Code Examples
#1 Code Example with C++ Programming
Code -
C++ Programming
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> findRedundantConnection(vector < vector<int>>& edges) {
int tag = 1;
unordered_map < int, int>id;
unordered_map<int, vector<int>>g;
for(auto x: edges){
int u = x[0], v = x[1];
g[u].push_back(v);
g[v].push_back(u);
if(id[u] && id[v] && id[u] == id[v]) return x;
else if(!id[u] && !id[v]) id[u] = id[v] = tag++;
else if(id[u]) DFS(g, id, v, id[u]);
else id[u] = id[v];
}
}
void DFS(unordered_map < int, vector<int>>& g, unordered_map < int, int>& id, int root, int tag){
if(id[root] == tag) return;
id[root] = tag;
for(auto x: g[root]) DFS(g, id, x, tag);
}
};
Input
Output
#2 Code Example with Javascript Programming
Code -
Javascript Programming
const findRedundantConnection = function (edges) {
const uf = {}
for (let edge of edges) {
let u = edge[0]
let v = edge[1]
if (find(u) === find(v)) {
return edge
} else {
union(u, v)
}
}
function union(a, b) {
uf[find(a)] = uf[find(b)]
}
function find(x) {
if (!uf[x]) uf[x] = x
if (uf[x] === x) return x
return find(uf[x])
}
}
Input
Output
#3 Code Example with Python Programming
Code -
Python Programming
class Solution:
def findRedundantConnection(self, edges: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
parent = [0] * len(edges)
def find(x):
if parent[x] == 0:
return x
parent[x] = find(parent[x])
return parent[x]
def union(x, y):
rootX = find(x)
rootY = find(y)
if rootX == rootY:
return False
parent[rootX] = rootY
return True
res = [0, 0]
for x, y in edges:
if not union(x - 1, y - 1):
res = [x, y]
return res
Input
Output
