Algorithm
Problem Name: 701. Insert into a Binary Search Tree
You are given the root node of a binary search tree (BST) and a value to insert into the tree. Return the root node of the BST after the insertion. It is guaranteed that the new value does not exist in the original BST.
Notice that there may exist multiple valid ways for the insertion, as long as the tree remains a BST after insertion. You can return any of them.
Example 1:
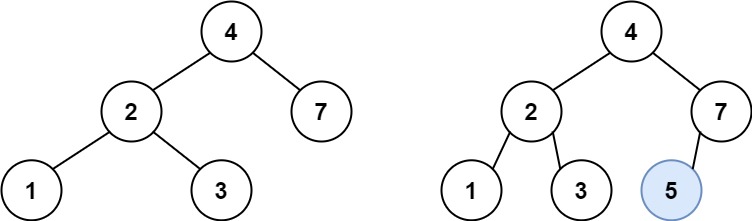
Input: root = [4,2,7,1,3], val = 5 Output: [4,2,7,1,3,5] Explanation: Another accepted tree is: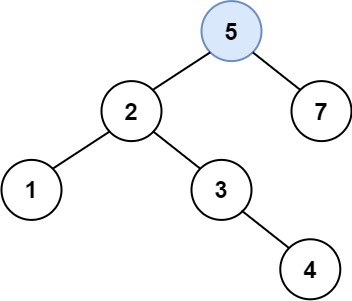
Example 2:
Input: root = [40,20,60,10,30,50,70], val = 25 Output: [40,20,60,10,30,50,70,null,null,25]
Example 3:
Input: root = [4,2,7,1,3,null,null,null,null,null,null], val = 5 Output: [4,2,7,1,3,5]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree will be in the range
[0, 104]. -108 <= Node.val <= 108- All the values
Node.valare unique. -108 <= val <= 108- It's guaranteed that
valdoes not exist in the original BST.
Code Examples
#1 Code Example with C++ Programming
Code -
C++ Programming
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* insertIntoBST(TreeNode* root, int val) {
dfs(root, val);
return root;
}
void dfs(TreeNode*& root, int val) {
if (!root) {
root = new TreeNode(val);
return;
}
if (root->val > val) {
dfs(root->left, val);
} else {
dfs(root->right, val);
}
}
};
Input
Output
#2 Code Example with Java Programming
Code -
Java Programming
class Solution {
public TreeNode insertIntoBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
TreeNode node = root;
while (node != null) {
if (val > node.val) {
if (node.right == null) {
node.right = new TreeNode(val);
return root;
} else {
node = node.right;
}
} else {
if (node.left == null) {
node.left = new TreeNode(val);
return root;
} else {
node = node.left;
}
}
}
return new TreeNode(val);
}
}
Input
Output
#3 Code Example with Javascript Programming
Code -
Javascript Programming
const insertIntoBST = function(root, val) {
if(root == null) return new TreeNode(val);
let cur = root;
while(true) {
if(cur.val <= val) {
if(cur.right != null) cur = cur.right;
else {
cur.right = new TreeNode(val);
break;
}
} else {
if(cur.left != null) cur = cur.left;
else {
cur.left = new TreeNode(val>;
break;
}
}
}
return root;
};
Input
Output
#4 Code Example with Python Programming
Code -
Python Programming
class Solution:
def insertIntoBST(self, root, val):
if root and root.val > val and not self.insertIntoBST(root.left, val): root.left = TreeNode(val)
elif root and root.val < val and not self.insertIntoBST(root.right, val): root.right = TreeNode(val)
return root
Input
Output
#5 Code Example with C# Programming
Code -
C# Programming
namespace LeetCode
{
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* public int val;
* public TreeNode left;
* public TreeNode right;
* public TreeNode(int val=0, TreeNode left=null, TreeNode right=null) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
public class _0701_InsertIntoABinarySearchTree
{
public TreeNode InsertIntoBST(TreeNode root, int val)
{
if (root == null) return new TreeNode(val);
var node = root;
while (node != null)
{
if (val < node.val)
{
if (node.left == null)
{
node.left = new TreeNode(val);
return root;
}
else
node = node.left;
}
else
{
if (node.right == null)
{
node.right = new TreeNode(val);
return root;
}
else
node = node.right;
}
}
return root;
}
}
}
Input
Output
