Algorithm
Problem Name: 437. Path Sum III
Given the root of a binary tree and an integer targetSum, return the number of paths where the sum of the values along the path equals targetSum.
The path does not need to start or end at the root or a leaf, but it must go downwards (i.e., traveling only from parent nodes to child nodes).
Example 1:
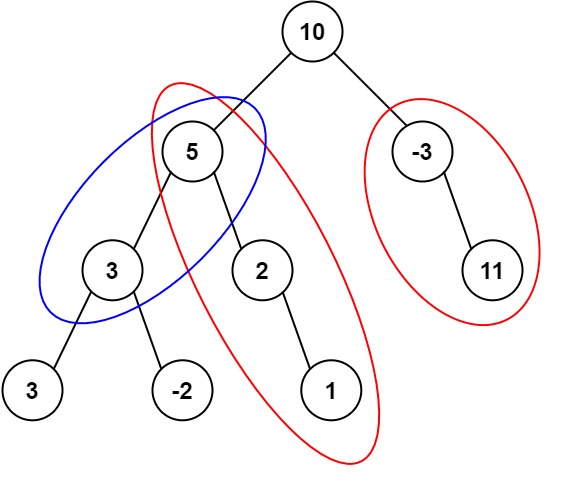
Input: root = [10,5,-3,3,2,null,11,3,-2,null,1], targetSum = 8 Output: 3 Explanation: The paths that sum to 8 are shown.
Example 2:
Input: root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,5,1], targetSum = 22 Output: 3
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 1000]. -109 <= Node.val <= 109-1000 <= targetSum <= 1000
Code Examples
#1 Code Example with C Programming
Code -
C Programming
int sumFrom(struct TreeNode *node, int sum) {
int n = 0;
if (node) {
sum -= node->val;
n += (!sum) ? 1 : 0;
n += sumFrom(node->left, sum);
n += sumFrom(node->right, sum);
}
return n;
}
int pathSum(struct TreeNode* root, int sum) {
if (!root) return 0;
return sumFrom(root, sum) +
pathSum(root->left, sum) +
pathSum(root->right, sum);
}
Input
Output
#2 Code Example with Java Programming
Code -
Java Programming
class Solution {
public int pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
Map map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(0L, 1);
int[] count = {0};
preorder(root, 0L, map, count, targetSum);
return count[0];
}
private void preorder(TreeNode root, long currSum, Map < Long, Integer> map, int[] count, int targetSum) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
currSum += root.val;
count[0] += map.getOrDefault(currSum - targetSum, 0);
map.put(currSum, map.getOrDefault(currSum, 0) + 1);
preorder(root.left, currSum, map, count, targetSum);
preorder(root.right, currSum, map, count, targetSum);
map.put(currSum, map.get(currSum) - 1);
}
}
Input
Output
#3 Code Example with Javascript Programming
Code -
Javascript Programming
function pathSum(root, sum) {
const preSums = new Map([[0, 1]]);
let count = 0;
visit(root, 0);
return count;
function visit(node, preSum) {
if (!node) return;
preSum += node.val;
count += preSums.get(preSum - sum) || 0;
preSums.set(preSum, (preSums.get(preSum) || 0) + 1);
visit(node.left, preSum);
visit(node.right, preSum);
preSums.set(preSum, preSums.get(preSum) - 1);
}
}
Input
Output
#4 Code Example with Python Programming
Code -
Python Programming
class Solution:
def pathSum(self, root, sum):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:type sum: int
:rtype: int
"""
dic = {}
def traverse(node, parent):
if not node: return
dic[node] = [node.val]
if node.val == sum: res[0] += 1
if parent:
for num in dic[parent]:
dic[node].append(num + node.val)
if num + node.val == sum: res[0] += 1
traverse(node.left, node)
traverse(node.right, node)
res = [0]
traverse(root, None)
return res[0]
Input
Output
#5 Code Example with C# Programming
Code -
C# Programming
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace LeetCode
{
public class _0437_PathSumIII
{
public int result;
public int PathSum(TreeNode root, int sum)
{
if (root == null) return 0;
Dictionary < int, int> cache = new Dictionary<int, int>() { { 0, 1 } };
DFS(root, sum, 0, cache);
return result;
}
public void DFS(TreeNode root, int target, int currPathSum, Dictionary < int, int> cache)
{
if (root == null) return;
currPathSum += root.val;
int oldPathSum = currPathSum - target;
if (cache.ContainsKey(oldPathSum)) result += cache[oldPathSum];
if (!cache.ContainsKey(currPathSum))
cache.Add(currPathSum, 0);
cache[currPathSum]++;
DFS(root.left, target, currPathSum, cache);
DFS(root.right, target, currPathSum, cache);
cache[currPathSum] -= 1;
}
}
}
Input
Output
