Algorithm
Problem Name: 883. Projection Area of 3D Shapes
You are given an n x n grid where we place some 1 x 1 x 1 cubes that are axis-aligned with the x, y, and z axes.
Each value v = grid[i][j] represents a tower of v cubes placed on top of the cell (i, j).
We view the projection of these cubes onto the xy, yz, and zx planes.
A projection is like a shadow, that maps our 3-dimensional figure to a 2-dimensional plane. We are viewing the "shadow" when looking at the cubes from the top, the front, and the side.
Return the total area of all three projections.
Example 1:
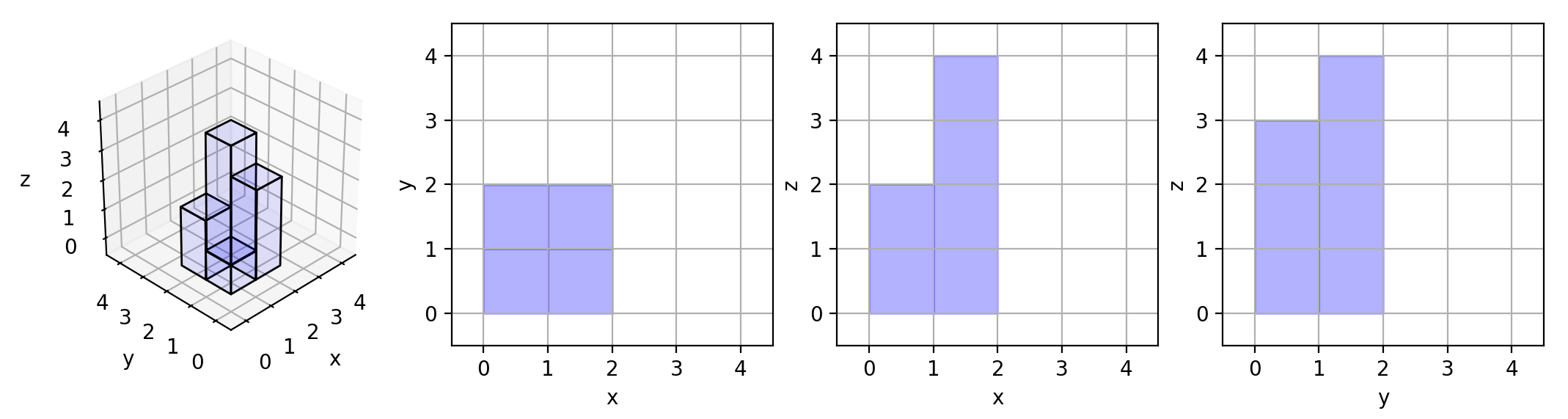
Input: grid = [[1,2],[3,4]]
Output: 17
Explanation: Here are the three projections ("shadows") of the shape made with each axis-aligned plane.
Example 2:
Input: grid = [[2]] Output: 5
Example 3:
Input: grid = [[1,0],[0,2]] Output: 8
Constraints:
n == grid.length == grid[i].length1 <= n <= 500 <= grid[i][j] <= 50
Code Examples
#1 Code Example with Java Programming
Code -
Java Programming
class Solution {
public int projectionArea(int[][] grid) {
int sum = 0;
for (int i=0; i < grid.length; i++) {
int maxRow = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int maxCol = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int j=0; j < grid[i].length; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] > 0) {
sum++;
}
maxRow = Math.max(maxRow, grid[i][j]);
maxCol = Math.max(maxCol, grid[j][i]);
}
sum += maxCol + maxRow;
}
return sum;
}
}
Input
Output
#2 Code Example with Javascript Programming
Code -
Javascript Programming
const projectionArea = function(grid) {
let xy = 0, xz = 0, yz = 0
const m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length
for (let i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for(let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if(grid[i][j]) xy++
}
}
for (let i = 0; i < m; i++) {
let tmp = 0
for(let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
tmp = Math.max(tmp, grid[i][j])
}
xz += tmp
}
for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
let tmp = 0
for(let i = 0; i < m; i++) {
tmp = Math.max(tmp, grid[i][j]>
}
yz += tmp
}
return xy + yz + xz
};
Input
Output
#3 Code Example with Python Programming
Code -
Python Programming
class Solution:
def projectionArea(self, grid):
"""
:type grid: List[List[int]]
:rtype: int
"""
n = len(grid)
top = sum(grid[i][j] != 0 for i in range(n) for j in range(n))
front = sum(max(grid[i]) for i in range(n))
side = sum(max(grid[i][j] for i in range(n)) for j in range(n))
return top + front + side
Input
Output
#4 Code Example with C# Programming
Code -
C# Programming
using System;
namespace LeetCode
{
public class _0883_ProjectionAreaOf3DShapes
{
public int ProjectionArea(int[][] grid)
{
var N = grid.Length;
var result = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
int bestRow = 0, bestCol = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
if (grid[i][j] > 0) result++;
bestRow = Math.Max(bestRow, grid[i][j]);
bestCol = Math.Max(bestCol, grid[j][i]);
}
result += bestRow + bestCol;
}
return result;
}
}
}
Input
Output
