Algorithm
Problem Name: 687. Longest Univalue Path
Given the root of a binary tree, return the length of the longest path, where each node in the path has the same value. This path may or may not pass through the root.
The length of the path between two nodes is represented by the number of edges between them.
Example 1:
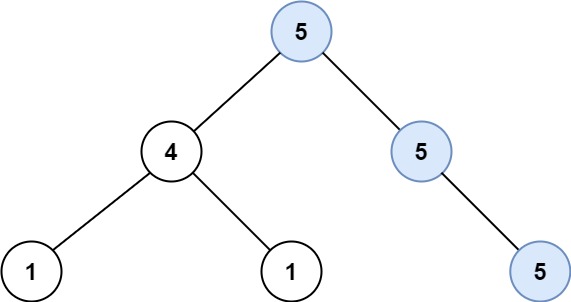
Input: root = [5,4,5,1,1,null,5] Output: 2 Explanation: The shown image shows that the longest path of the same value (i.e. 5).
Example 2:
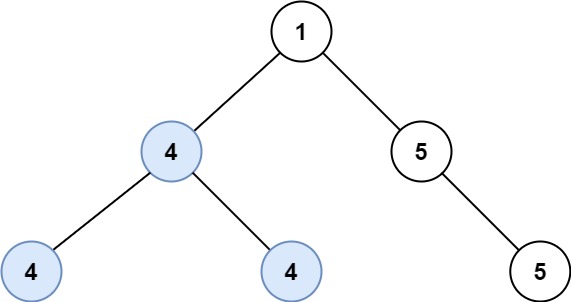
Input: root = [1,4,5,4,4,null,5] Output: 2 Explanation: The shown image shows that the longest path of the same value (i.e. 4).
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 104]. -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000- The depth of the tree will not exceed
1000.
Code Examples
#1 Code Example with C Programming
Code -
C Programming
int helper(struct TreeNode *node, int *max) {
int l, r, k;
if (!node) return 0;
l = helper(node->left, max);
r = helper(node->right, max);
k = 1;
if (l && node->val == node->left->val) {
k += l;
l ++;
} else {
l = 1;
}
if (node->right && node->val == node->right->val) {
k += r;
r ++;
} else {
r = 1;
}
if (*max < k) *max = k;
return l > r ? l : r;
}
int longestUnivaluePath(struct TreeNode* root) {
int max = 1;
helper(root, &max);
return max - 1;
}
Input
Output
#2 Code Example with C++ Programming
Code -
C++ Programming
class Solution {
public:
int longestUnivaluePath(TreeNode* root) {
int maxlen = 0;
DFS(root, maxlen);
return maxlen;
}
int DFS(TreeNode* root, int& maxlen){
if(!root) return 0;
int left = DFS(root->left, maxlen);
int right = DFS(root->right, maxlen);
if(!root->left || root->left->val != root->val) left = 0;
if(!root->right || root->right->val != root->val) right = 0;
maxlen = max(maxlen, left + right);
return max(left, right) + 1;
}
};
Input
Output
#3 Code Example with Javascript Programming
Code -
Javascript Programming
const longestUnivaluePath = function(root) {
let res = 0
dfs(root)
return res
function dfs(node) {
if(node == null) return 0
let left = dfs(node.left), right = dfs(node.right)
if(node.left && node.left.val === node.val) left++
else left = 0
if(node.right && node.right.val === node.val) right++
else right = 0
res = Math.max(res, left + right)
return Math.max(left, right)
}
};
Input
Output
#4 Code Example with C# Programming
Code -
C# Programming
using System;
namespace LeetCode
{
public class _0687_LongestUnivaluePath
{
private int result = 0;
public int LongestUnivaluePath(TreeNode root)
{
result = 0;
GetLenght(root);
return result;
}
private int GetLenght(TreeNode node)
{
if (node == null) return 0;
var leftLength = GetLenght(node.left);
var rightLength = GetLenght(node.right);
if (node.left != null && node.left.val == node.val)
leftLength++;
else
leftLength = 0;
if (node.right != null && node.right.val == node.val)
rightLength++;
else
rightLength = 0;
result = Math.Max(result, leftLength + rightLength);
return Math.Max(leftLength, rightLength);
}
}
}
Input
Output
