Algorithm
Problem Nmae: 113. Path Sum II
Given the root of a binary tree and an integer targetSum, return all root-to-leaf paths where the sum of the node values in the path equals targetSum. Each path should be returned as a list of the node values, not node references.
A root-to-leaf path is a path starting from the root and ending at any leaf node. A leaf is a node with no children.
Example 1:
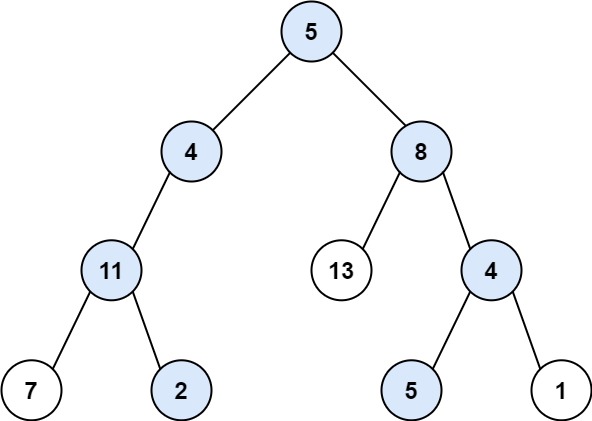
Input: root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,5,1], targetSum = 22 Output: [[5,4,11,2],[5,8,4,5]] Explanation: There are two paths whose sum equals targetSum: 5 + 4 + 11 + 2 = 22 5 + 8 + 4 + 5 = 22
Example 2:

Input: root = [1,2,3], targetSum = 5 Output: []
Example 3:
Input: root = [1,2], targetSum = 0 Output: []
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 5000]. -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000-1000 <= targetSum <= 1000
Code Examples
#1 Code Example with C++ Programming
Code -
C++ Programming
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int sum) {
vector < vector<int>>res;
if(!root) return res;
DFS(root, res, vector<int>(), 0, sum);
return res;
}
void DFS(TreeNode* root, vector<vector < int>>& res, vector<int>path, int sum, int target){
if(!root> return;
path.push_back(root->val);
sum += root->val;
if(!root->left && !root->right){
if(sum == target) res.push_back(path);
return;
}
DFS(root->left, res, path, sum, target);
DFS(root->right, res, path, sum, target);
}
};
Input
Output
#2 Code Example with Java Programming
Code -
Java Programming
class Solution {
public List();
if (root == null) {
return result;
}
Queue < NodePathSumWrapper> queue = new LinkedList<>();
NodePathSumWrapper currNode = new NodePathSumWrapper(root, 0);
currNode.addToPath(root.val);
queue.add(currNode);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
while (size-- > 0) {
NodePathSumWrapper removed = queue.remove();
TreeNode node = removed.node;
if (node.left == null && node.right == null) {
if (removed.currSum == targetSum) {
result.add(new ArrayList < >(removed.path));
}
} else {
if (node.left != null) {
NodePathSumWrapper leftNodeWrapper = new NodePathSumWrapper(node.left, removed.currSum);
leftNodeWrapper.path.addAll(removed.path);
leftNodeWrapper.addToPath(node.left.val);
queue.add(leftNodeWrapper);
}
if (node.right != null) {
NodePathSumWrapper rightNodeWrapper = new NodePathSumWrapper(node.right, removed.currSum);
rightNodeWrapper.path.addAll(removed.path);
rightNodeWrapper.addToPath(node.right.val);
queue.add(rightNodeWrapper);
}
}
}
}
return result;
}
private static class NodePathSumWrapper {
TreeNode node;
int currSum;
List < Integer> path;
public NodePathSumWrapper(TreeNode node, int currSum) {
this.node = node;
this.currSum = currSum;
this.path = new ArrayList < >();
}
public void addToPath(int value) {
this.path.add(value);
this.currSum += value;
}
}
}
Input
Output
#3 Code Example with Javascript Programming
Code -
Javascript Programming
const pathSum = function(root, sum) {
const result = [];
backtrack(root, sum, [], result);
return result;
};
const backtrack = function(root, sum, temp, result) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
temp.push(root.val);
let newSum = sum - root.val;
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
if (newSum === 0) {
result.push([...temp]);
}
temp.pop();
return;
}
backtrack(root.left, newSum, temp, result);
backtrack(root.right, newSum, temp, result);
temp.pop();
}
Input
Output
#4 Code Example with Python Programming
Code -
Python Programming
class Solution:
def pathSum(self, root, sum):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:type sum: int
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
def traverse(node, q, residue, res = []):
if node:
if not node.left and not node.right and residue + node.val == sum: res.append(q + [node.val])
traverse(node.left, q + [node.val], residue + node.val)
traverse(node.right, q + [node.val], residue + node.val)
return res
return traverse(root, [], 0)
Input
Output
#5 Code Example with C# Programming
Code -
C# Programming
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace LeetCode
{
public class _113_PathSum2
{
public IList < IList<int>> PathSum(TreeNode root, int sum)
{
var current = new List < int>();
var results = new List current, IList(current));
current.RemoveAt(current.Count - 1);
return;
}
PathSum(root.left, sum, current, results);
PathSum(root.right, sum, current, results);
current.RemoveAt(current.Count - 1);
}
}
}
Input
Output
