Algorithm
Problem Name: 834. Sum of Distances in Tree
Problem Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/sum-of-distances-in-tree/
There is an undirected connected tree with n nodes labeled from 0 to n - 1 and n - 1 edges.
You are given the integer n and the array edges where edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ai and bi in the tree.
Return an array answer of length n where answer[i] is the sum of the distances between the ith node in the tree and all other nodes.
Example 1:
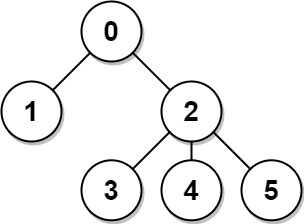
Input: n = 6, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[2,3],[2,4],[2,5]] Output: [8,12,6,10,10,10] Explanation: The tree is shown above. We can see that dist(0,1) + dist(0,2) + dist(0,3) + dist(0,4) + dist(0,5) equals 1 + 1 + 2 + 2 + 2 = 8. Hence, answer[0] = 8, and so on.
Example 2:

Input: n = 1, edges = [] Output: [0]
Example 3:
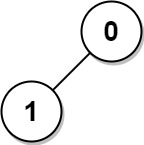
Input: n = 2, edges = [[1,0]] Output: [1,1]
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 3 * 104edges.length == n - 1edges[i].length == 20 <= ai, bi < nai != bi- The given input represents a valid tree.
Code Examples
#1 Code Example with C++ Programming
Code -
C++ Programming
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> sumOfDistancesInTree(int N, vector < vector<int>>& edges) {
vector < vector<int>>g(N, vector<int>());
for(auto& e: edges){
g[e[0]].push_back(e[1]);
g[e[1]].push_back(e[0]);
}
vector<int>res(N), child(N), visited(N);
dfs(g, res, child, 0, 0, visited);
for(auto& x: visited) x = 0;
dfs(g, res, child, 0, visited, N);
return res;
}
// Sum of the distances of node 0
void dfs(vector < vector<int>>& g, vector<int>& res, vector<int>& child, int len, int root, vector<int>& visited){
visited[root] = 1;
res[0] += len++;
for(auto& x: g[root]){
if(visited[x]) continue;
dfs(g, res, child, len, x, visited);
child[root] += child[x];
}
child[root] += 1;
}
// Sum of the distances of node 1 to N - 1
void dfs(vector<vector < int>>& g, vector<int>& res, vector<int>& child, int root, vector<int>& visited, int N){
visited[root] = 1;
for(auto& x: g[root]){
if(visited[x]) continue;
res[x] = res[root] - child[x] + N - child[x];
dfs(g, res, child, x, visited, N>;
}
}
};
Input
Output
#2 Code Example with Javascript Programming
Code -
Javascript Programming
const sumOfDistancesInTree = function (N, edges) {
const graph = createGraph(N, edges)
const counts = new Array(N).fill(0)
const dists = new Array(N).fill(0)
dists[0] = getCount(graph, 0, -1, counts).sum
return transferDist(N, graph, 0, -1, counts, dists)
}
function transferDist(N, graph, u, pre, counts, dists) {
if (pre >= 0) {
const nRight = counts[u]
const nLeft = N - nRight
dists[u] = dists[pre] - nRight + nLeft
}
for (const v of graph[u]) {
if (v !== pre) {
transferDist(N, graph, v, u, counts, dists)
}
}
return dists
}
function getCount(graph, u, pre, counts) {
const output = { nNodes: 0, sum: 0 }
for (const v of graph[u]) {
if (v !== pre) {
const result = getCount(graph, v, u, counts)
output.nNodes += result.nNodes
output.sum += result.nNodes + result.sum
}
}
output.nNodes += 1
counts[u] = output.nNodes
return output
}
function createGraph(N, edges) {
const graph = new Array(N).fill(null).map(() => [])
for (const [u, v] of edges) {
graph[u].push(v)
graph[v].push(u)
}
return graph
}
Input
Output
#3 Code Example with Python Programming
Code -
Python Programming
class Solution:
def sumOfDistancesInTree(self, N, edges):
tree = collections.defaultdict(set)
res = [0] * N
count = [1] * N
for i, j in edges:
tree[i].add(j)
tree[j].add(i)
def dfs(root, pre):
for i in tree[root]:
if i != pre:
dfs(i, root)
count[root] += count[i]
res[root] += res[i] + count[i]
def dfs2(root, pre):
for i in tree[root]:
if i != pre:
res[i] = res[root] - count[i] + N - count[i]
dfs2(i, root)
dfs(0, -1)
dfs2(0, -1)
return res
Input
Output
