Algorithm
Problem Name: 833. Find And Replace in String
You are given a 0-indexed string s that you must perform k replacement operations on. The replacement operations are given as three 0-indexed parallel arrays, indices, sources, and targets, all of length k.
To complete the ith replacement operation:
- Check if the substring
sources[i]occurs at indexindices[i]in the original strings. - If it does not occur, do nothing.
- Otherwise if it does occur, replace that substring with
targets[i].
For example, if s = "abcd", indices[i] = 0, sources[i] = "ab", and targets[i] = "eee", then the result of this replacement will be "eeecd".
All replacement operations must occur simultaneously, meaning the replacement operations should not affect the indexing of each other. The testcases will be generated such that the replacements will not overlap.
- For example, a testcase with
s = "abc",indices = [0, 1], andsources = ["ab","bc"]will not be generated because the"ab"and"bc"replacements overlap.
Return the resulting string after performing all replacement operations on s.
A substring is a contiguous sequence of characters in a string.
Example 1:

Input: s = "abcd", indices = [0, 2], sources = ["a", "cd"], targets = ["eee", "ffff"] Output: "eeebffff" Explanation: "a" occurs at index 0 in s, so we replace it with "eee". "cd" occurs at index 2 in s, so we replace it with "ffff".
Example 2:
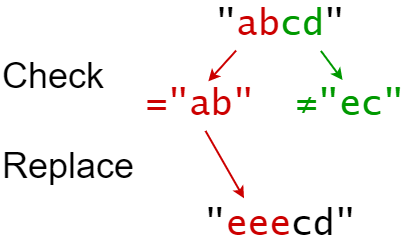
Input: s = "abcd", indices = [0, 2], sources = ["ab","ec"], targets = ["eee","ffff"] Output: "eeecd" Explanation: "ab" occurs at index 0 in s, so we replace it with "eee". "ec" does not occur at index 2 in s, so we do nothing.
Constraints:
1 <= s.length <= 1000k == indices.length == sources.length == targets.length1 <= k <= 1000 <= indexes[i] < s.length1 <= sources[i].length, targets[i].length <= 50sconsists of only lowercase English letters.sources[i]andtargets[i]consist of only lowercase English letters.
Code Examples
#1 Code Example with C Programming
Code -
C Programming
typedef struct {
int i;
char *s;
char *t;
} e_t;
int cmp(const void *a, const void *b) {
const e_t *e1 = a;
const e_t *e2 = b;
if (e1->i < e2->i) return -1;
if (e1->i > e2->i) return 1;
return 0;
}
char * findReplaceString(char * S, int* indexes, int indexesSize, char ** sources, int sourcesSize, char ** targets, int targetsSize){
int sz, i, j, l, k;
char *buff, *newbuff, *p, *o, *s, *t;
e_t e[100];
for (i = 0; i < indexesSize; i ++) {
e[i].i = indexes[i];
e[i].s = sources[i];
e[i].t = targets[i];
}
qsort(e, indexesSize, sizeof(*e), cmp);
sz = 1000;
buff = malloc(sz * sizeof(char));
//assert(buff);
o = S;
p = buff;
p[0] = 0;
for (i = 0; i < indexesSize; i ++) {
j = e[i].i;
l = j - (o - S);
if (l > 0) {
if (p - buff + l >= sz) {
sz *= 2;
newbuff = realloc(buff, sz * sizeof(char));
//assert(newbuff);
p = &newbuff[p - buff];
buff = newbuff;
}
strncpy(p, o, l);
o += l;
p += l;
p[0] = 0; // add null
}
s = e[i].s;
l = strlen(s);
t = e[i].t;
if (!strncmp(o, s, l)) {
k = strlen(t);
if (p - buff + k >= sz) {
sz *= 2;
newbuff = realloc(buff, sz * sizeof(char));
//assert(newbuff);
p = &newbuff[p - buff];
buff = newbuff;
}
strcat(p, t);
o += l;
p += k;
}
}
l = strlen(S) - (o - S);
if (l > 0) {
if (p - buff + l >= sz) {
sz *= 2;
newbuff = realloc(buff, sz * sizeof(char));
//assert(newbuff);
p = &newbuff[p - buff];
buff = newbuff;
}
strcat(p, o);
}
return buff;
}
Input
Output
#2 Code Example with Java Programming
Code -
Java Programming
class Solution {
public String findReplaceString(String S, int[] indexes, String[] sources, String[] targets) {
Map map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < indexes.length; i++) {
map.put(indexes[i], new String[]{sources[i], targets[i]});
}
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < S.length(); i++) {
if (map.containsKey(i)) {
String source = map.get(i)[0];
String target = map.get(i)[1];
int currIdx = 0;
boolean mismatch = false;
while (currIdx + i < S.length() && currIdx < source.length()) {
if (source.charAt(currIdx) != S.charAt(currIdx + i)) {
mismatch = true;
break;
}
currIdx++;
}
if (mismatch || currIdx != source.length()) {
sb.append(S.charAt(i));
continue;
}
sb.append(target);
i += source.length() - 1;
}
else {
sb.append(S.charAt(i));
}
}
return sb.toString();
}
}
Input
Output
#3 Code Example with Python Programming
Code -
Python Programming
class Solution:
def findReplaceString(self, s, indexes, sources, targets):
res, dic, j = "", {}, 0
for i in range(len(sources)):
if s.find(sources[i], indexes[i]) == indexes[i]: dic[indexes[i]] = (sources[i], targets[i])
while j < len(s):
res += j in dic and dic[j][1] or s[j]
j += j in dic and len(dic[j][0]) or 1
return res
Input
Output
#4 Code Example with C# Programming
Code -
C# Programming
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace LeetCode
{
public class _0833_FindAndReplaceInString
{
public string FindReplaceString(string S, int[] indexes, string[] sources, string[] targets)
{
var N = S.Length;
var match = new int[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
match[i] = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < indexes.Length; i++)
if (S.Substring(indexes[i], sources[i].Length).SequenceEqual(sources[i]))
match[indexes[i]] = i;
var sb = new StringBuilder();
var index = 0;
while (index < N)
{
if (match[index] > -1)
{
sb.Append(targets[match[index]]);
index += sources[match[index]].Length;
}
else
{
sb.Append(S[index++]);
}
}
return sb.ToString();
}
}
}
Input
Output
